Setting a relation¶
This operation creates a relationship between a parent and child objects. If the parent object already has other related children, the relationship is reset - the child objects identified in this operation become the sole children of the parent. If you're looking for an operation which adds child objects to an existing set of children, see the Adding to a relation chapter of this guide.
Important
It is important that the relation column in the parent table is created before a transaction with the operation runs.
Specific Children¶
There are multiple "flavors" of this operation, but in its core, it must reference a parent object and one or more child objects. The parent object must have a valid objectIdvalue. The APIs are grouped below by how the parent object is identified - using objectId, as a map, as an instance of a custom class or as a result of a previous operation in the same transaction:
// Set the objects identified with objectId values in the childrenObjectId array
// as children of the parent object identified with parentObjectId. The parent
// object must be in the table with the parentTableName name. The relationship
// column between the parent and child objects is columnName. In other words,
// for the relationship represented through the columnName column, set the child
// objects to the parent object. Both child and parent objects are identified with
// objectId values.
unitOfWork.setRelation( tableName: string,
parentObjectId: string,
columnName: string,
objectIds: string[] );
// Same as the above with the only difference is the child objects are instances
// of a custom class (YourCustomClassForChild). It is important that
// YourCustomClassForChild matches the child table name. For example, if the
// relationship is between tables Person and Address, then the
// YourCustomClassForChild class must be "Address".
unitOfWork.setRelation( tableName: string,
parentObject: object,
columnName: string,
children: object[] );
// Set the objects represented by the "children" argument as the children of the
// parent object. The parent object is identified by its objectId with the
// parentObjectId argument. The parent object must be stored in a table with the
// parentTableName name. The "children" argument is a result of a previous operation
// in the same transaction. It must represent either a collection of string values
// (objectIds) or a collection of objects. This is possible with the following
// previous operations:
// - Retrieving objects from the database
// - Saving multiple objects in the database
// It is important that all child objects referenced by the children argument exist
// in the child table that columnName points to.
unitOfWork.setRelation( tableName: string,
parentObjectId: string,
columnName: string,
children: OpResult );
// Set the objects from the childrenObjectId array as children of parentObject.
// The array must contain objectId values of the child obbjects. The parent
// object must be in the table with the parentTableName name. The relationship
// column between the parent and child objects is columnName. In other words,
// for the relationship represented through the columnName column, set the
// child objects to the parent object. The parent object is a map of key/value
// pairs. One of the pairs must be objectId with the corresponding value. The
// children are identified with their objectId values.
unitOfWork.setRelation( tableName: string,
parentObject: object,
columnName: string,
childrenObjectId: string[] );
// Same as the above with the only difference is the child objects are instannces
// of a custom class. It is important that the class of the children objects
// matches the child table name. For example, if the relationship is between
// tables Person and Address, then the class of children objects must be "Address".
unitOfWork.setRelation( tableName: string,
parentObject: object,
columnName: string,
children: object[] );
// Set the objects represented by the "children" argument as the children of
// the parent object. The parent object must have the "objectid" key.
// The parent object must be stored in a table with the parentTableName name.
// The "children" argument is a result of a previous operation in the same
// transaction. It must represent either a collection of string values (objectIds)
// or a collection of objects. This is possible with the following previous operations:
// - Retrieving objects from the database
// - Saving multiple objects in the database
// It is important that all child objects referenced by the children argument
// exist in the child table that columnName points to.
unitOfWork.setRelation( tableName: string,
parentObject: object,
columnName: string,
children: OpResult );
// Set the objects identified with objectId values in the objectIds
// array as children of parentObject. The relationship column between the
// parent and child objects is "columnName". The parent object must have the
// "objectId" key with a valid value. The child objects are identified
// with their objectId values. Since the parent object is an instance of
// a develoepor-defined class, it means the parent table where the parent
// object is stored must match the name of the class.
// For example, if the parentObject class is "Person", it means
// Backendless wiil:
// 1. Look for the parent object in the Person table using "objectId" key
// in parentObject.
// 2. Locate a column with the columnName name in the Person table
// 3. Using the column definition, Backendless will identify the child table
// 4. Backendless will retrieve the child objects from the child table using
// the provided objectId values.
// 5. Backendless wiill set the relationship between the child objects and
// the parent object.
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentObject: object,
columnName: string,
objectIds: string[] );
// Same as the first signature above with the only difference is the child
// objects are not strings. It is important that each child object has the
// "objectId" key with a valid value.
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentObject: object,
columnName: string,
children: object[] );
// Same as the first signature above with the only difference is the children
// argument is a result of a previous operation in the same transaction. It
// must represent either a collection of string values (objectIds) or a
// collection of objects. This is possible with the following previous
// operations:
// - Retrieving objects from the database
// - Saving multiple objects in the database
// It is important that all child objects referenced by the children argument
// exist in the child table that columnName points to.
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentObject: object,
columnName: string,
children: OpResult );
// Set the children identified with their objectId values from the
// childrenObjectId array as the related children of parentObject. The
// parentObject value is a result of a previous operation in the same
// transaction. These operations can be:
// - Saving a single object in the database
// - Updating a single object in the database
// The relationship is identified through the column with the name in the
// columnName argument. The column must be declared in the same table where
// parentObject comes from. It is important that all child objects in the
// childrenObjectId array exist in the child table that columnName points to.
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentObject: OpResult,
columnName: string,
childrenObjectId: string[] );
// Same as the first signature above with the only difference is the child
// objects are not strings. It is important that each child object has the
// "objectId" key with a valid value.
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentObject: OpResult,
columnName: string,
children: object[] );
// In this operation both the parent and the children objects are results of
// two separate previous operations in the same transaction. The parent
// object must be a result of any of the following operations:
// - Saving a single object in the database
// - Updating a single object in the database
// The relationship is identified through the column with the name in the
// columnName argument. The column must be declared in the same table where
// parentObject comes from. The children argument can be a result of the
// following operations:
// - Retrieving objects from the database
// - Saving multiple objects in the database
// It is important that all child objects referenced by the children argument
// exist in the child table that columnName points to.
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentObject: OpResult,
columnName: string,
children: OpResult );
Children with a Query¶
There are APIs where the child objects can be identified with a query using a where clause. These APIs run a query to get the child objects and then sets them to the parent in the relation. Again the APIs are grouped by how the parent object is identified:
// Set the objects identified by whereClauseForChildren as children of the parent
// object identified with parentObjectId. The parent object must be in the table
// with the parentTableName name. The relationship column between the parent and
// child objects is columnName. The whereClauseForChildren query is executed in
// the child table that columnName points to.
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentTableName: string,
parentObjectId: string,
columnName: string,
whereClauseForChildren: string );
// Set the objects identified by whereClauseForChildren as children of the parent
// object represented by parentObject. The parent object must be in the
// table with the parentTableName name. The relationship column between the parent
// and child objects is columnName. The whereClauseForChildren query is executed
// in the child table that the columnName column points to.
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentTableName: string,
parentObject: object,
columnName: string,
whereClauseForChildren: string );
// Set the objects identified by whereClauseForChildren as
// children of the parent. The relationship column between
// the parent and child objects is columnName. Since the
// parent object is an instance of a developer-defined
// class, it means the parent table where the parent object
// is stored must match the name of the class. For example,
// if the class of parentObject is "Person", it means
// Backendless wiil:
// 1. Look for the parent object in the Person table.
// 2. Locate a column with the columnName name in the
// Person table.
// 3. Using the column definition, Backendless will
// identify the child table.
// 4. Backendless will run the whereClauseForChildren
// query in the child table to identify the child
// objects.
// 5. Backendless wiil establish the relationship between
// the child objects and the parent object.
// The class of parentObject must have the "objectId" key
// with a valid value. The child objects are identified with
// their objectId values.
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentObject: object,
columnName: string,
whereClauseForChildren: string );
// Set the objects identified by the whereClauseForChildren query as children
// of the parent object. The parentObject value is a result of a previous
// operation in the same transaction. These operations can be:
// - Saving a single object in the database
// - Updating a single object in the database
// The relationship is identified through the column with the name in the
// columnName argument. The column must be declared in the same table where
// parentObject comes from. For example, if the parent object is stored in a
// table called "Person", Backendless wiil:
// 1. Look for the parent object in the Person table
// 2. Locate a column with the columnName name in the Person table
// 3. Using the column definition, Backendless will identify the child table
// 4. Backendless will run the whereClauseForChildren query in the child table
// to identify the child objects
// 5. Backendless wiill establish the relationship between the child objects
// and the parent object.
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentObject: OpResult,
columnName: string,
whereClauseForChildren: string );
// Same as the above except the parentObject is a reference to an object within
// a result of annother operation in the same transaction. For example, a
// result of another operation can be a collection of objects. That collection
// can be returning from either the "Retrieving objects" or "Saving multiple
// objetcs" operations. Using the OpResult API you can obtain a single object
// which can be used as parent in this operation. When a single object from a
// collection represented by OpResult is referenced, it is represented by the
// OpResultValueReference class.
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentObject: OpResultValueReference,
columnName: string,
whereClauseForChildren: string );
Return Value¶
The operation returns an OpResult object which represents the result of this operation - number of child objects set in the relation.
Examples¶
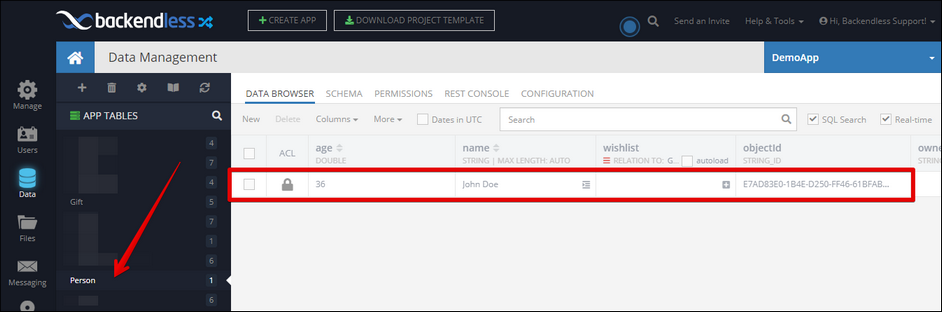
All examples below perform the same operation of linking objects from the Gift table to an object from the Person table through a column called wishlist. This is what the parent table looks like:
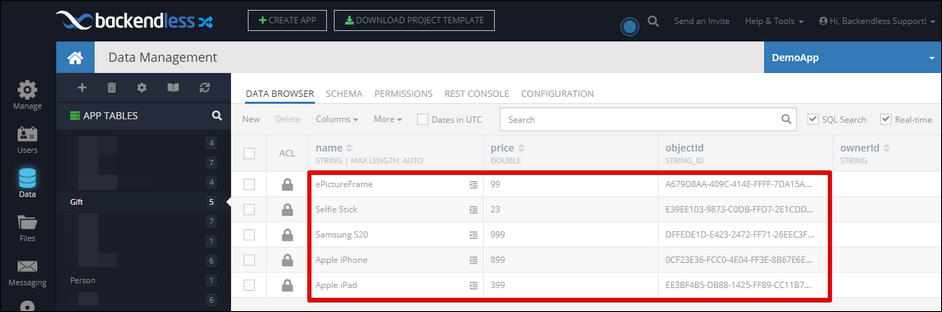
You can see the wishlist column, which is a one-to-many relation with the Gift table shown below:
The examples are organized by two levels: first is how the parent object is represented in the client program, then by the type of the child collection.
Parent object is represented as
** The child objects are represented as**
const unitOfWork = new Backendless.UnitOfWork();
// This is an array for child objects.
// They are referenced using objectId values.
// The example hard-codes the array, but in
// your code you'd get the objectId values
// from your data model or using a query
const giftIds = [
"EE3BF4B5-DB88-1425-FF89-CC11B7707500",
"0CF23E36-FCC0-4E04-FF3E-8B67E6E27200",
"DFFEDE1D-E423-2472-FF71-26EEC3F23700"
]
// this is the objectId of the parent object.
const personObjectId = "E7AD83E0-1B4E-D250-FF46-61BFAB18D700";
// the name of the table where the parent object is stored
const parentTableName = "Person";
// the name of the relation column
const relationColumnName = "wishlist";
// add the setRelation call to the transaction
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentTableName,
personObjectId,
relationColumnName,
giftIds );
// run the transaction
unitOfWork.execute()
.then(function (unitOfWorkResult) {
// transaction is complete. Use uowResult to check the result
})
.catch( function( error ) {
// Server reported an error.
});
const unitOfWork = new Backendless.UnitOfWork();
// This is a list of gift objects. These objects
// will be children in the relationship. As you
// can see the objects are constructed manually
// and their objectId's are set, however, in your
// application they would be loaded from the
// server. This is done here to keep the example
// more succinct.
const gifts = [
{objectId : "EE3BF4B5-DB88-1425-FF89-CC11B7707500"},
{objectId : "0CF23E36-FCC0-4E04-FF3E-8B67E6E27200"}
]
// the name of the table where the parent object is stored
const parentTableName = "Person";
// the name of the relation column
const relationColumnName = "wishlist";
// add the setRelation call to the transaction
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentTableName,
personObjectId,
relationColumnName,
gifts );
// run the transaction
unitOfWork.execute()
.then(function (unitOfWorkResult) {
// transaction is complete. Use uowResult to check the result
})
.catch( function( error ) {
// Server reported an error.
});
const unitOfWork = new Backendless.UnitOfWork();
// This is an array for child objects.
// They are referenced using objectId values.
// The example hard-codes the array, but in
// your code you'd get the objectId values
// from your data model or using a query
const gifts = [
new Gift({"objectId" : "EE3BF4B5-DB88-1425-FF89-CC11B7707500"}),
new Gift({"objectId" : "0CF23E36-FCC0-4E04-FF3E-8B67E6E27200"})
]
// this is the objectId of the parent object.
const personObjectId = "E7AD83E0-1B4E-D250-FF46-61BFAB18D700";
// the name of the table where the parent object is stored
const parentTableName = "Person";
// the name of the relation column
const relationColumnName = "wishlist";
// add the setRelation call to the transaction
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentTableName,
personObjectId,
relationColumnName,
gifts );
// run the transaction
unitOfWork.execute()
.then(function (unitOfWorkResult) {
// transaction is complete. Use uowResult to check the result
})
.catch( function( error ) {
// Server reported an error.
});
function Gift(args) {
args = args || {};
this.objectId = args.objectId || "";
this.name = args.name || "";
this.price = args.price || "";
}
const unitOfWork = new Backendless.UnitOfWork();
// compose a query to fetch the gift objects
const queryBuilder = Backendless.DataQueryBuilder.create();
queryBuilder.setWhereClause("name in ( 'Apple iPad', 'Apple iPhone', 'Selfie Stick')" );
// add the find operation to the transaction
// notice the result of the operation is saved in a constiable -
// it will be used further in the setRelation operation
const gifts = unitOfWork.find("Gift", queryBuilder);
// this is the objectId of the parent object.
const personObjectId = "E7AD83E0-1B4E-D250-FF46-61BFAB18D700";
// the name of the table where the parent object is stored
const parentTableName = "Person";
// the name of the relation column
const relationColumnName = "wishlist";
// add the setRelation call to the transaction
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentTableName,
personObjectId,
relationColumnName,
gifts );
// run the transaction
unitOfWork.execute()
.then(function (unitOfWorkResult) {
// transaction is complete. Use uowResult to check the result
})
.catch( function( error ) {
// Server reported an error.
});
** The child objects are represented as**
const unitOfWork = new Backendless.UnitOfWork();
// This is an array for child objects.
// They are referenced using objectId values.
// The example hard-codes the array, but in
// your code you'd get the objectId values
// from your data model or using a query
const giftIds = [
"EE3BF4B5-DB88-1425-FF89-CC11B7707500",
"0CF23E36-FCC0-4E04-FF3E-8B67E6E27200",
"DFFEDE1D-E423-2472-FF71-26EEC3F23700"
]
// this is the objectId of the parent object.
const personObjectId = {"objectId" : "E7AD83E0-1B4E-D250-FF46-61BFAB18D700"}
// the name of the table where the parent object is stored
const parentTableName = "Person";
// the name of the relation column
const relationColumnName = "wishlist";
// add the setRelation call to the transaction
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentTableName,
personObjectId,
relationColumnName,
giftIds );
// run the transaction
unitOfWork.execute()
.then(function (unitOfWorkResult) {
// transaction is complete. Use uowResult to check the result
})
.catch( function( error ) {
// Server reported an error.
});
const unitOfWork = new Backendless.UnitOfWork();
// This is a list of gift objects. These objects
// will be children in the relationship. As you
// can see the objects are constructed manually
// and their objectId's are set, however, in your
// application they would be loaded from the
// server. This is done here to keep the example
// more succinct.
const gifts = [
{"objectId" : "EE3BF4B5-DB88-1425-FF89-CC11B7707500"},
{"objectId" : "0CF23E36-FCC0-4E04-FF3E-8B67E6E27200"}
]
// this is the objectId of the parent object.
const personObjectId = {"objectId" : "E7AD83E0-1B4E-D250-FF46-61BFAB18D700"}
// the name of the table where the parent object is stored
const parentTableName = "Person";
// the name of the relation column
const relationColumnName = "wishlist";
// add the setRelation call to the transaction
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentTableName,
personObjectId,
relationColumnName,
gifts );
// run the transaction
unitOfWork.execute()
.then(function (unitOfWorkResult) {
// transaction is complete. Use uowResult to check the result
})
.catch( function( error ) {
// Server reported an error.
});
const unitOfWork = new Backendless.UnitOfWork();
// This is an array for child objects.
// They are referenced using objectId values.
// The example hard-codes the array, but in
// your code you'd get the objectId values
// from your data model or using a query
const gifts = [
new Gift({"objectId" : "EE3BF4B5-DB88-1425-FF89-CC11B7707500"}),
new Gift({"objectId" : "0CF23E36-FCC0-4E04-FF3E-8B67E6E27200"})
]
// this is the objectId of the parent object.
const personObjectId = {"objectId" : "E7AD83E0-1B4E-D250-FF46-61BFAB18D700"}
// the name of the table where the parent object is stored
const parentTableName = "Person";
// the name of the relation column
const relationColumnName = "wishlist";
// add the setRelation call to the transaction
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentTableName,
personObjectId,
relationColumnName,
gifts );
// run the transaction
unitOfWork.execute()
.then(function (unitOfWorkResult) {
// transaction is complete. Use uowResult to check the result
})
.catch( function( error ) {
// Server reported an error.
});
function Gift(args) {
args = args || {};
this.objectId = args.objectId || "";
this.name = args.name || "";
this.price = args.price || "";
}
const unitOfWork = new Backendless.UnitOfWork();
// compose a query to fetch the gift objects
const queryBuilder = Backendless.DataQueryBuilder.create();
queryBuilder.setWhereClause("name in ( 'Apple iPad', 'Apple iPhone', 'Selfie Stick')" );
// add the find operation to the transaction
// notice the result of the operation is saved in a constiable -
// it will be used further in the setRelation operation
const gifts = unitOfWork.find("Gift", queryBuilder);
// this is the objectId of the parent object.
const personObjectId = {"objectId" : "E7AD83E0-1B4E-D250-FF46-61BFAB18D700"}
// the name of the table where the parent object is stored
const parentTableName = "Person";
// the name of the relation column
const relationColumnName = "wishlist";
// add the setRelation call to the transaction
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentTableName,
personObjectId,
relationColumnName,
gifts );
// run the transaction
unitOfWork.execute()
.then(function (unitOfWorkResult) {
// transaction is complete. Use uowResult to check the result
})
.catch( function( error ) {
// Server reported an error.
});
** The child objects are represented as**
const unitOfWork = new Backendless.UnitOfWork();
// This is an array for child objects.
// They are referenced using objectId values.
// The example hard-codes the array, but in
// your code you'd get the objectId values
// from your data model or using a query
const giftIds = [
"EE3BF4B5-DB88-1425-FF89-CC11B7707500",
"0CF23E36-FCC0-4E04-FF3E-8B67E6E27200",
"DFFEDE1D-E423-2472-FF71-26EEC3F23700"
]
// this is the objectId of the parent object.
const personObjectId = new Person({"objectId" : "E7AD83E0-1B4E-D250-FF46-61BFAB18D700"});
// the name of the table where the parent object is stored
const parentTableName = "Person";
// the name of the relation column
const relationColumnName = "wishlist";
// add the setRelation call to the transaction
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentTableName,
personObjectId,
relationColumnName,
giftIds );
// run the transaction
unitOfWork.execute()
.then(function (unitOfWorkResult) {
// transaction is complete. Use uowResult to check the result
})
.catch( function( error ) {
// Server reported an error.
});
const unitOfWork = new Backendless.UnitOfWork();
// This is a list of gift objects. These objects
// will be children in the relationship. As you
// can see the objects are constructed manually
// and their objectId's are set, however, in your
// application they would be loaded from the
// server. This is done here to keep the example
// more succinct.
const gifts = [
{"objectId" : "EE3BF4B5-DB88-1425-FF89-CC11B7707500"},
{"objectId" : "0CF23E36-FCC0-4E04-FF3E-8B67E6E27200"}
]
// this is the objectId of the parent object.
const personObjectId = new Person({"objectId" : "E7AD83E0-1B4E-D250-FF46-61BFAB18D700"});
// the name of the table where the parent object is stored
const parentTableName = "Person";
// the name of the relation column
const relationColumnName = "wishlist";
// add the setRelation call to the transaction
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentTableName,
personObjectId,
relationColumnName,
gifts );
// run the transaction
unitOfWork.execute()
.then(function (unitOfWorkResult) {
// transaction is complete. Use uowResult to check the result
})
.catch( function( error ) {
// Server reported an error.
});
const unitOfWork = new Backendless.UnitOfWork();
// This is an array for child objects.
// They are referenced using objectId values.
// The example hard-codes the array, but in
// your code you'd get the objectId values
// from your data model or using a query
const gifts = [
new Gift({"objectId" : "EE3BF4B5-DB88-1425-FF89-CC11B7707500"}),
new Gift({"objectId" : "0CF23E36-FCC0-4E04-FF3E-8B67E6E27200"})
]
// this is the objectId of the parent object.
const personObjectId = new Person({"objectId" : "E7AD83E0-1B4E-D250-FF46-61BFAB18D700"});
// the name of the table where the parent object is stored
const parentTableName = "Person";
// the name of the relation column
const relationColumnName = "wishlist";
// add the setRelation call to the transaction
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentTableName,
personObjectId,
relationColumnName,
gifts );
// run the transaction
unitOfWork.execute()
.then(function (unitOfWorkResult) {
// transaction is complete. Use uowResult to check the result
})
.catch( function( error ) {
// Server reported an error.
});
function Gift(args) {
args = args || {};
this.objectId = args.objectId || "";
this.name = args.name || "";
this.price = args.price || "";
}
const unitOfWork = new Backendless.UnitOfWork();
// compose a query to fetch the gift objects
const queryBuilder = Backendless.DataQueryBuilder.create();
queryBuilder.setWhereClause("name in ( 'Apple iPad', 'Apple iPhone', 'Selfie Stick')" );
// add the find operation to the transaction
// notice the result of the operation is saved in a constiable -
// it will be used further in the setRelation operation
const gifts = unitOfWork.find("Gift", queryBuilder);
// this is the objectId of the parent object.
const personObjectId = new Person({"objectId" : "E7AD83E0-1B4E-D250-FF46-61BFAB18D700"});
// the name of the table where the parent object is stored
const parentTableName = "Person";
// the name of the relation column
const relationColumnName = "wishlist";
// add the setRelation call to the transaction
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentTableName,
personObjectId,
relationColumnName,
gifts );
// run the transaction
unitOfWork.execute()
.then(function (unitOfWorkResult) {
// transaction is complete. Use uowResult to check the result
})
.catch( function( error ) {
// Server reported an error.
});
** The child objects are represented as**
const unitOfWork = new Backendless.UnitOfWork();
// This is an array for child objects.
// They are referenced using objectId values.
// The example hard-codes the array, but in
// your code you'd get the objectId values
// from your data model or using a query
const giftIds = [
"EE3BF4B5-DB88-1425-FF89-CC11B7707500",
"0CF23E36-FCC0-4E04-FF3E-8B67E6E27200",
"DFFEDE1D-E423-2472-FF71-26EEC3F23700"
]
// compose a query to retrieve the person
// from the database
const queryBuilder = Backendless.DataQueryBuilder.create();
// this is the query which identifies the person of interest,
// this person object will be used as the parent in the relationship
queryBuilder.setWhereClause( "name = 'John Doe' and age = 36" );
// add the object retrieval operation to the transaction
const findResult = unitOfWork.find( "Person", queryBuilder );
// since "findResult" references a collection of objects,
// get the first one from the collection. The reason we need to
// do this is because the setRelation operation below
// expects only one parent object. We know the first object
// will be the parent, that's why the "resolveTo" index is 0.
const parentObjectRef = findResult.resolveTo( 0 );
// the name of the relation column
const relationColumnName = "wishlist";
// add the setRelation call to the transaction
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentObjectRef,
relationColumnName,
giftIds );
// run the transaction
unitOfWork.execute()
.then(function (unitOfWorkResult) {
// transaction is complete. Use uowResult to check the result
})
.catch( function( error ) {
// Server reported an error.
});
const unitOfWork = new Backendless.UnitOfWork();
// This is a list of gift objects. These objects
// will be children in the relationship. As you
// can see the objects are constructed manually
// and their objectId's are set, however, in your
// application they would be loaded from the
// server. This is done here to keep the example
// more succinct.
const gifts = [
{"objectId" : "EE3BF4B5-DB88-1425-FF89-CC11B7707500"},
{"objectId" : "0CF23E36-FCC0-4E04-FF3E-8B67E6E27200"}
]
// compose a query to retrieve the person
// from the database
const queryBuilder = Backendless.DataQueryBuilder.create();
// this is the query which identifies the person of interest,
// this person object will be used as the parent in the relationship
queryBuilder.setWhereClause( "name = 'John Doe' and age = 36" );
// add the object retrieval operation to the transaction
const findResult = unitOfWork.find( "Person", queryBuilder );
// since "findResult" references a collection of objects,
// get the first one from the collection. The reason we need to
// do this is because the setRelation operation below
// expects only one parent object. We know the first object
// will be the parent, that's why the "resolveTo" index is 0.
const parentObjectRef = findResult.resolveTo( 0 );
// the name of the relation column
const relationColumnName = "wishlist";
// add the setRelation call to the transaction
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentObjectRef,
relationColumnName,
gifts );
// run the transaction
unitOfWork.execute()
.then(function (unitOfWorkResult) {
// transaction is complete. Use uowResult to check the result
})
.catch( function( error ) {
// Server reported an error.
});
const unitOfWork = new Backendless.UnitOfWork();
// This is an array for child objects.
// They are referenced using objectId values.
// The example hard-codes the array, but in
// your code you'd get the objectId values
// from your data model or using a query
const gifts = [
new Gift({"objectId" : "EE3BF4B5-DB88-1425-FF89-CC11B7707500"}),
new Gift({"objectId" : "0CF23E36-FCC0-4E04-FF3E-8B67E6E27200"})
]
// compose a query to retrieve the person
// from the database
const queryBuilder = Backendless.DataQueryBuilder.create();
// this is the query which identifies the person of interest,
// this person object will be used as the parent in the relationship
queryBuilder.setWhereClause( "name = 'John Doe' and age = 36" );
// add the object retrieval operation to the transaction
const findResult = unitOfWork.find( "Person", queryBuilder );
// since "findResult" references a collection of objects,
// get the first one from the collection. The reason we need to
// do this is because the setRelation operation below
// expects only one parent object. We know the first object
// will be the parent, that's why the "resolveTo" index is 0.
const parentObjectRef = findResult.resolveTo( 0 );
// the name of the relation column
const relationColumnName = "wishlist";
// add the setRelation call to the transaction
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentObjectRef,
relationColumnName,
gifts );
// run the transaction
unitOfWork.execute()
.then(function (unitOfWorkResult) {
// transaction is complete. Use uowResult to check the result
})
.catch( function( error ) {
// Server reported an error.
});
function Gift(args) {
args = args || {};
this.objectId = args.objectId || "";
this.name = args.name || "";
this.price = args.price || "";
}
const unitOfWork = new Backendless.UnitOfWork();
// compose a query to fetch the gift objects
const queryBuilder = Backendless.DataQueryBuilder.create();
queryBuilder.setWhereClause("name in ( 'Apple iPad', 'Apple iPhone', 'Selfie Stick')" );
// add the find operation to the transaction
// notice the result of the operation is saved in a constiable -
// it will be used further in the setRelation operation
const gifts = unitOfWork.find("Gift", queryBuilder);
// compose a query to retrieve the person
// from the database
const queryBuilder = Backendless.DataQueryBuilder.create();
// this is the query which identifies the person of interest,
// this person object will be used as the parent in the relationship
queryBuilder.setWhereClause( "name = 'John Doe' and age = 36" );
// add the object retrieval operation to the transaction
const findResult = unitOfWork.find( "Person", queryBuilder );
// since "findResult" references a collection of objects,
// get the first one from the collection. The reason we need to
// do this is because the setRelation operation below
// expects only one parent object. We know the first object
// will be the parent, that's why the "resolveTo" index is 0.
const parentObjectRef = findResult.resolveTo( 0 );
// the name of the relation column
const relationColumnName = "wishlist";
// add the setRelation call to the transaction
unitOfWork.setRelation( parentObjectRef,
relationColumnName,
gifts );
// run the transaction
unitOfWork.execute()
.then(function (unitOfWorkResult) {
// transaction is complete. Use uowResult to check the result
})
.catch( function( error ) {
// Server reported an error.
});
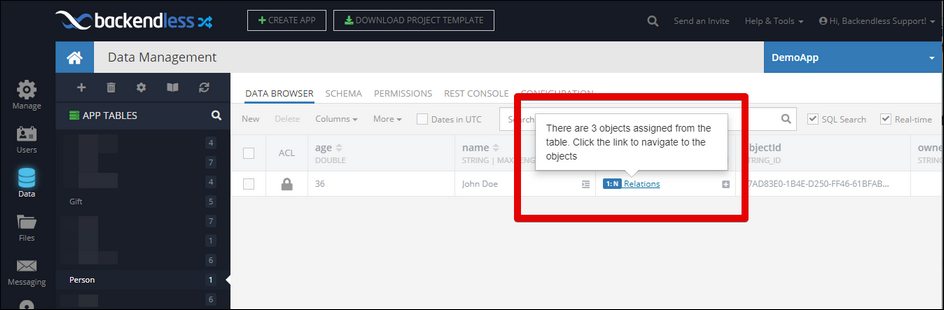
The screenshot below is what the Person object will look like in Backendless Console. Notice the wishlist relation column now indicates there are related child objects: