Retrieving Unique Objects¶
Unique objects can be retrieved from a column of the requested table by setting the true value in the setDistinct method, The distinct parameter is a boolean value which defaults to false.
The distinct property can be also used with Aggregate Functions such as AVERAGE, COUNT, and SUM. When applied to an aggregate function, the distinct property ensures that only distinct values are considered in the calculation, eliminating any duplicates from the result.
For example, when using the distinct property with the COUNT function, it counts only the unique occurrences of a particular column, disregarding any repetitions. Similarly, when combined with AVERAGE or SUM, the distinct property ensures that only distinct values are considered in the calculation, providing accurate results based on unique values within the dataset.
Consider the following data table called Employees:
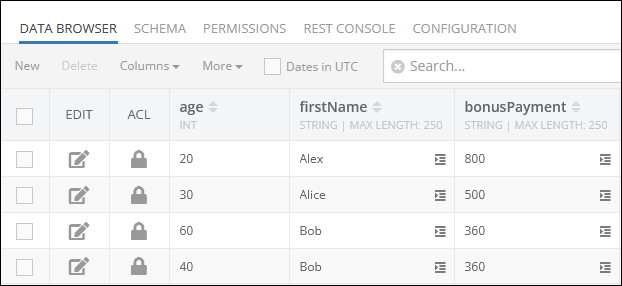
This table contains the column firstName, and by passing the true value to the setDistinct method, only unique values will be returned in the response:
const query = Backendless.DataQueryBuilder.create()
query.addProperty('firstName')
query.setDistinct(true)
const result = await Backendless.Data.of('Employees').find(query)
The query returns the following result which contains only unique names:
[
{
"___class": "Employees",
"firstName": "Alex"
},
{
"___class": "Employees",
"firstName": "Alice"
},
{
"___class": "Employees",
"firstName": "Bob"
}
]
Aggregate Functions¶
The distinct parameter can be also used with such aggregate functions as:
All examples presented further use sample data from the Employees data table presented in the beginning of this topic.
Average¶
Suppose you need to calculate an average value for a set of objects, but you want to skip identical records. The following example will retrieve only unique values from the age column and calculate the average age of all employees.
const query = Backendless.DataQueryBuilder.create()
query.addProperty('Avg(distinct age')
query.setDistinct(true)
const result = await Backendless.Data.of('Employees').find(query)
Count¶
The example below will count only unique values in the firstName column and return an integer value in the response:
const query = Backendless.DataQueryBuilder.create()
query.addProperty('Count(distinct firstName')
query.setDistinct(true)
const result = await Backendless.Data.of('Employees').find(query)
Sum¶
The example below will calculate the sum of unique values in the bonusPayment column and return an integer value in the response:
const query = Backendless.DataQueryBuilder.create()
query.addProperty('Sum(distinct bonusPayment')
query.setDistinct(true)
const result = await Backendless.Data.of('Employees').find(query)
Codeless Reference¶
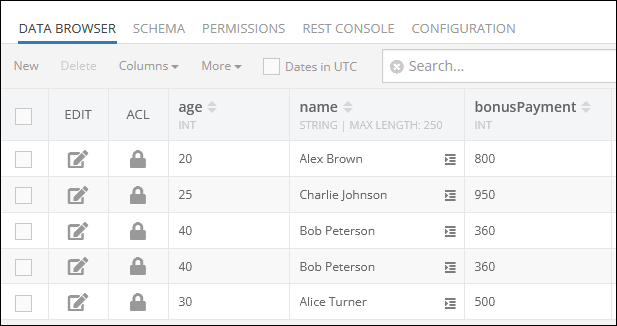
Consider the following data table called Employees:
AVERAGE¶
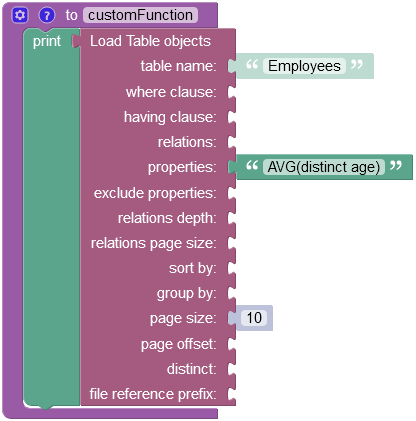
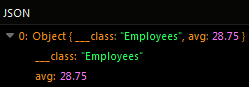
Suppose you need to calculate the average age of your employees, while excluding duplicates. As shown in the data table schema above, there are two identical records with the name "Bob Peterson". that have the value of 40 in the "age" column.
The example below returns the average age only for unique records stored in the Employees data table:
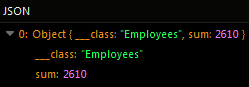
The operation returns the following result in the response:
COUNT¶
Suppose you need to count the number of employees, while excluding duplicates. Considering the data table schema provided above, there are two identical entities with the name "Bob Peterson".
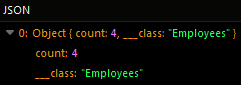
The example below counts the total number of unique employee names in the Employees data table:
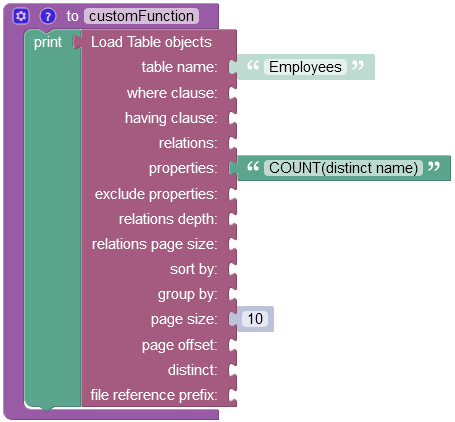
The operation returns the following result in the response:
SUM¶
Suppose you need to calculate the sum of all bonus payments, while excluding duplicates. Considering the data table schema provided above, there are two identical records that have the 360 value stored in the "bonusPayment" column:
The example below excludes the duplicate entity and calculates the sum of unique values:
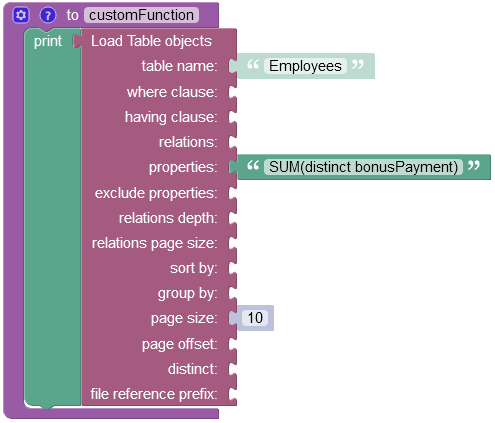
The operation returns the following result in the response: