Saving JSON Data¶
It is important to understand that JSON data in Backendless database are values stored in regular database objects. In order to take advantage of the JSON-specific APIs, the values must be stored in database column of the JSON type. Read how to create JSON columns. To add JSON data to the database, you can use either API or Backendless Console.
API¶
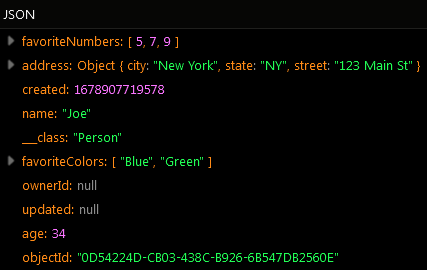
To store JSON with the API, you need to use the API to store single or multiple objects. Consider the following JSON document/object:
{
"name" : "Joe",
"age" : 34,
"address" : {
"street" : "123 Main St",
"city" : "New York",
"state": "New York"
},
"favoriteNumbers": [ 5,7,9,21,100 ],
"favoriteColors": [ "Blue", "Green" ]
}
The object includes another object (the "address" property), a property containing an array of numbers ("favoriteNumbers") and a property containing an array of string values ("favoriteColors"). The JSON object will be saved in the Person table in the profile column using the following request:
const result = await Backendless.Data.of('Person').save({
profile: {
name: 'Joe',
age : 34,
address : {
street: '123 Main St',
city : 'New York',
state : 'New York'
},
favoriteNumbers: [5, 7, 9, 21, 100],
favoriteColors : ['Blue', 'Green']
}
})
Backendless Console¶
JSON data can be added to your objects manually. Make sure to declare a JSON column in your database first. To add a JSON value, use the DATA BROWSER screen. You can work with the values in JSON columns as with plain text, however, entered value must be valid JSON. The database supports JSON string, number, object, array or null values.
Codeless Reference¶

where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
table name |
Name of the data table where a new record must be saved. |
object |
An object to save in the database. Object properties must match the names of the table columns. The object must not have the objectId property. |
return result |
Optional parameter. When this box is checked, the operation returns the saved object with the objectId property. |
Returns the saved object with the objectId property assigned by Backendless
Consider the following structure of the data table called Person :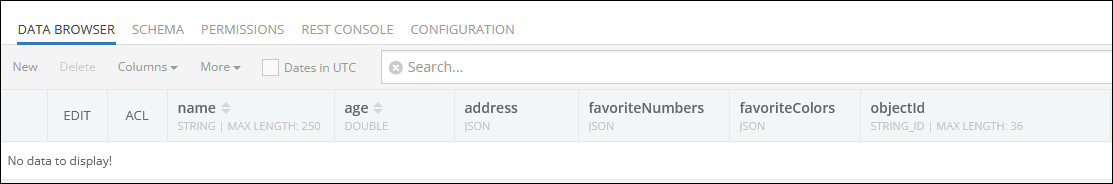
For demonstration purposes, the data table presented above has four custom columns: age, address, favoriteNumbers and favoriteColors. The former three columns have the default data type of JSON.
The objectId is a system column that contains unique identifiers of the records in the table. When a new record is saved to the table, the system assigns a unique objectId to it. The objectid is used in various operations as an access point to a specific record.
The example below saves a new JSON object to the Person data table:
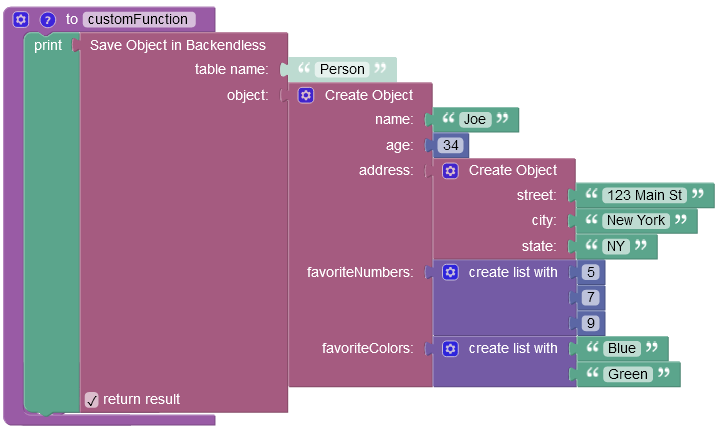
The result of this operation will look as shown below after the Codeless logic runs:
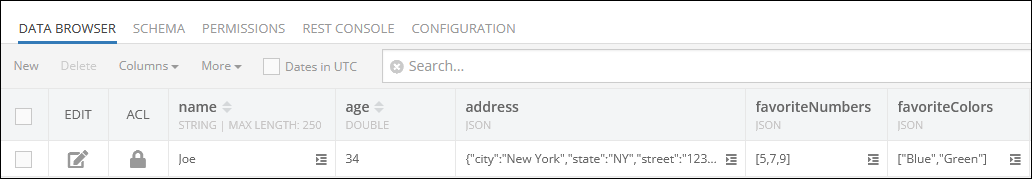
The operation described above has returned the newly saved object containing JSON data: