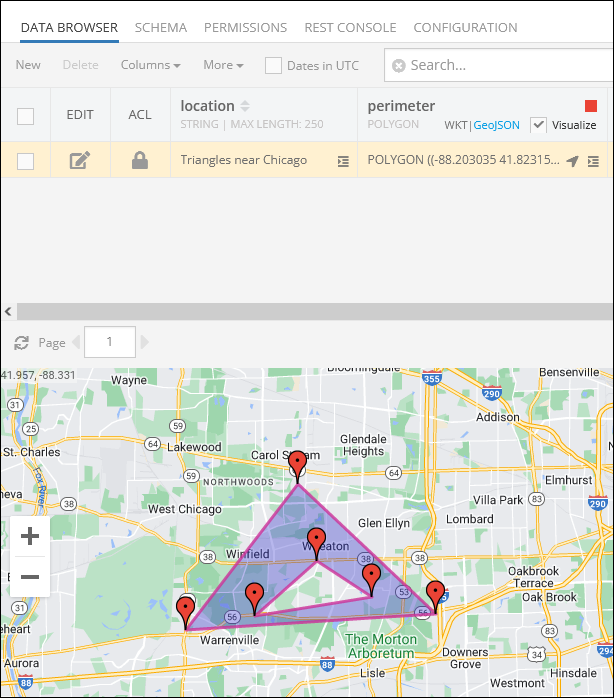
Spatial Data Create/Update API¶
Backendless SDK includes special classes which facilitate saving of spatial data values in the database. The same classes are used to represent spatial data when it is retrieved from the database. For more information about data retrieval, see the Spatial Data Retrieval API section.
POINT Values¶
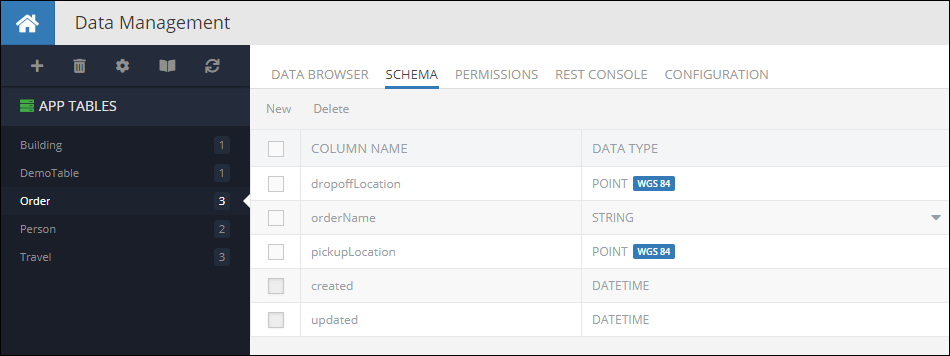
Consider the following table schema in Backendless database. Notice the pickupLocation and the dropoffLocation columns. Both are of type POINT:
The following code demonstrates how to create a new object with POINT properties in the Order table:
const order = {
orderName : 'Fun times',
pickupLocation : new Backendless.Data.Point().setLatitude(55.782309).setLongitude(37.578639),
dropoffLocation: new Backendless.Data.Point().setLatitude(55.752917).setLongitude(37.618900)
}
Backendless.Data.of('Order').save(order)
.then(savedOrder => {
const { objectId } = savedOrder
})
.catch(error => {
console.log(error)
})
Order class:
class Order {
constructor(props) {
this.objectId = null
this.orderName = null
this.pickupLocation = null
this.dropoffLocation = null
}
getObjectId() {
return this.objectId
}
setObjectId(objectId) {
return this.objectId = objectId
}
getPickupLocation() {
return this.pickupLocation
}
setPickupLocation(pickupLocation) {
this.pickupLocation = pickupLocation
}
getDropoffLocation() {
return this.dropoffLocation
}
setDropoffLocation(dropoffLocation) {
this.dropoffLocation = dropoffLocation
}
getOrderName() {
return this.orderName
}
setOrderName(orderName) {
this.orderName = orderName
}
}
const myOrder = new Order()
myOrder.setOrderName('Fun Times')
myOrder.setPickupLocation(new Backendless.Data.Point().setLatitude(55.782309).setLongitude(37.578639))
myOrder.setDropoffLocation(new Backendless.Data.Point().setLatitude(55.752917).setLongitude(37.618900))
Backendless.Data.mapTableToClass('Order', Order)
Backendless.Data.of(Order).save(myOrder)
.then(savedOrder => {
const objectId = savedOrder.getObjectId()
})
.catch(error => {
console.log(error)
})
Codeless Reference
The example below creates a new object containing two GeoJSON (Point) objects and saves it to the database called Order:
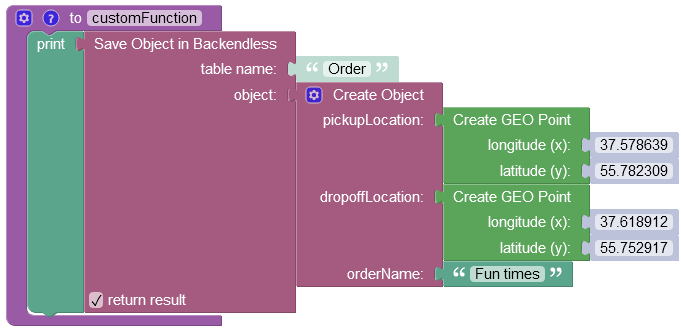
where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
table name |
Name of the data table where a new record must be saved. |
object |
An object to save in the database. Object properties must match the names of the table columns. The object must not have the objectId property. |
return result |
Optional parameter. When this box is checked, the operation returns the saved object with the objectId property. |
When you run the code(or Codeless logic), you will see the following in the database:
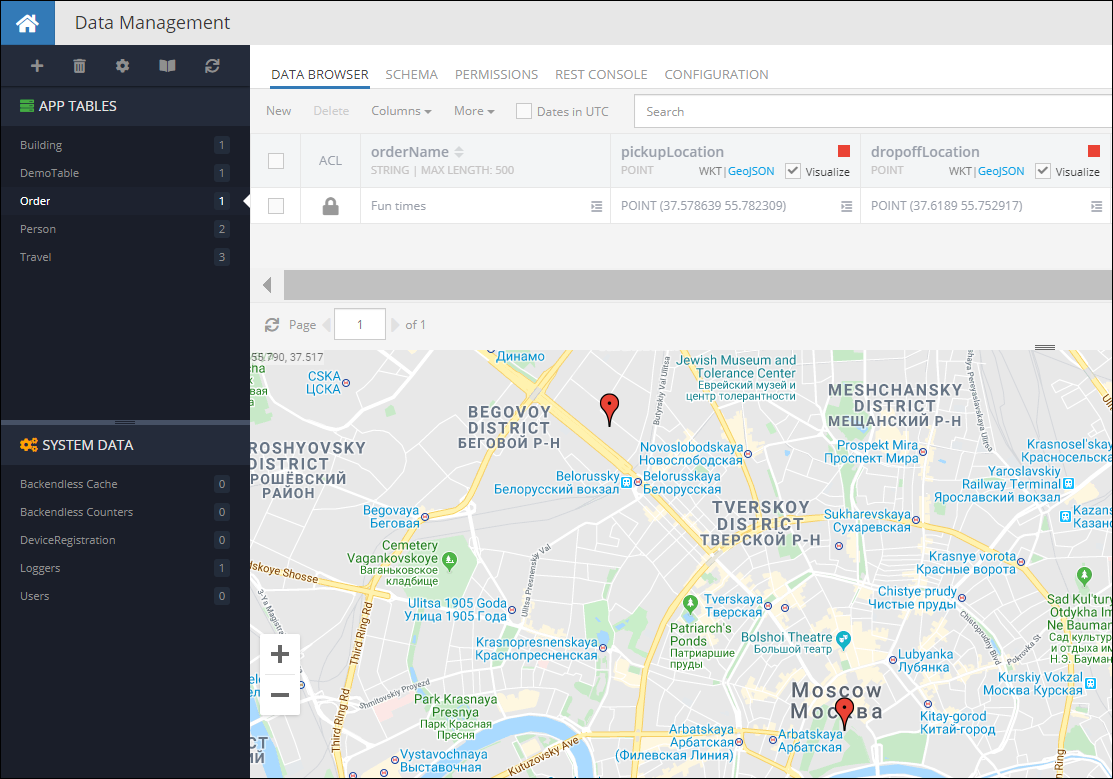
LINESTRING Values¶
Creating objects with LINESTRING properties works similarly to the example shown above - your code needs to use corresponding class from the SDK. For example, the code below creates an object in the Travel table with a LINESTRING route:
const route66LineString = 'LINESTRING (-87.52683788 41.85716752, ' +
'-90.13875858 38.68967135,' +
' -95.93953983 36.2131248, ' +
'-97.49959842 35.53656483, ' +
'-101.8282117 35.26791494, ' +
'-105.87118045 35.72083154, ' +
'-106.61825076 35.14794417, ' +
'-111.63900272 35.20182535, ' +
'-118.24178592 34.07195769)'
const path = Backendless.Data.LineString.fromWKT(route66LineString)
const travelObject = {
name : 'Route 66',
route: path
}
Backendless.Data.of('Travel').save(travelObject)
.then(savedObject => {
const { objectId } = savedObject
})
.catch(error => {
})
Travel class:
class Travel {
constructor() {
this.name = null
this.route = null
this.objectId = null
}
getName() {
return this.name
}
setName(name) {
this.name = name
}
getRoute() {
return this.route
}
setRoute(route) {
this.route = route
}
getObjectId() {
return this.objectId
}
setObjectId(objectId) {
this.objectId = objectId
}
}
const route66LineString = 'LINESTRING (-87.52683788 41.85716752, ' +
'-90.13875858 38.68967135,' +
' -95.93953983 36.2131248, ' +
'-97.49959842 35.53656483, ' +
'-101.8282117 35.26791494, ' +
'-105.87118045 35.72083154, ' +
'-106.61825076 35.14794417, ' +
'-111.63900272 35.20182535, ' +
'-118.24178592 34.07195769)'
const path = Backendless.Data.LineString.fromWKT(route66LineString)
const travelObject = new Travel()
travelObject.setName('Route 66')
travelObject.setRoute(path)
Backendless.Data.mapTableToClass('Travel', Travel)
Backendless.Data.of(Travel).save(travelObject)
.then(savedObject => {
const objectId = savedObject.getObjectId()
})
.catch(error => {
})
Notice the example above uses the LineString.fromWKT method to convert a string representation of a geometry into an instance of the LineString class. Alternatively, the code can use a constructor in the LineString class which takes an collection of Point objects. The example below and the one above produce exactly the same result using different approaches available in the SDK:
const travelObject = {
name: 'Route 66'
}
const points = []
const Point = Backendless.Data.Point
points.push(new Point().setLongitude(-90.13875858).setLatitude(38.68967135))
points.push(new Point().setLongitude(-95.93953983).setLatitude(36.2131248))
points.push(new Point().setLongitude(-97.49959842).setLatitude(35.53656483))
points.push(new Point().setLongitude(-101.8282117).setLatitude(35.26791494))
points.push(new Point().setLongitude(-105.87118045).setLatitude(35.72083154))
points.push(new Point().setLongitude(-106.61825076).setLatitude(35.14794417))
points.push(new Point().setLongitude(-111.63900272).setLatitude(35.20182535))
points.push(new Point().setLongitude(-118.24178592).setLatitude(34.07195769))
travelObject.route = new Backendless.Data.LineString(points)
Backendless.Data.of('Travel').save(travelObject)
.then(savedObject => {
const { objectId } = savedObject
})
.catch(error => {
})
Travel class:
class Travel {
constructor() {
this.name = null
this.route = null
this.objectId = null
}
getName() {
return this.name
}
setName(name) {
this.name = name
}
getRoute() {
return this.route
}
setRoute(route) {
this.route = route
}
getObjectId() {
return this.objectId
}
setObjectId(objectId) {
this.objectId = objectId
}
}
const points = []
const Point = Backendless.Data.Point
points.push(new Point().setLongitude(-90.13875858).setLatitude(38.68967135))
points.push(new Point().setLongitude(-95.93953983).setLatitude(36.2131248))
points.push(new Point().setLongitude(-97.49959842).setLatitude(35.53656483))
points.push(new Point().setLongitude(-101.8282117).setLatitude(35.26791494))
points.push(new Point().setLongitude(-105.87118045).setLatitude(35.72083154))
points.push(new Point().setLongitude(-106.61825076).setLatitude(35.14794417))
points.push(new Point().setLongitude(-111.63900272).setLatitude(35.20182535))
points.push(new Point().setLongitude(-118.24178592).setLatitude(34.07195769))
const travelObject = new Travel()
travelObject.setName('Route 66')
travelObject.setRoute(new Backendless.Data.LineString(points))
Backendless.Data.mapTableToClass('Travel', Travel)
Backendless.Data.of(Travel).save(travelObject)
.then(savedObject => {
const objectId = savedObject.getObjectId()
})
.catch(error => {
})
Codeless Reference
The example below creates a new object containing one GeoJSON (LineString) object and saves it to the database called Travel:
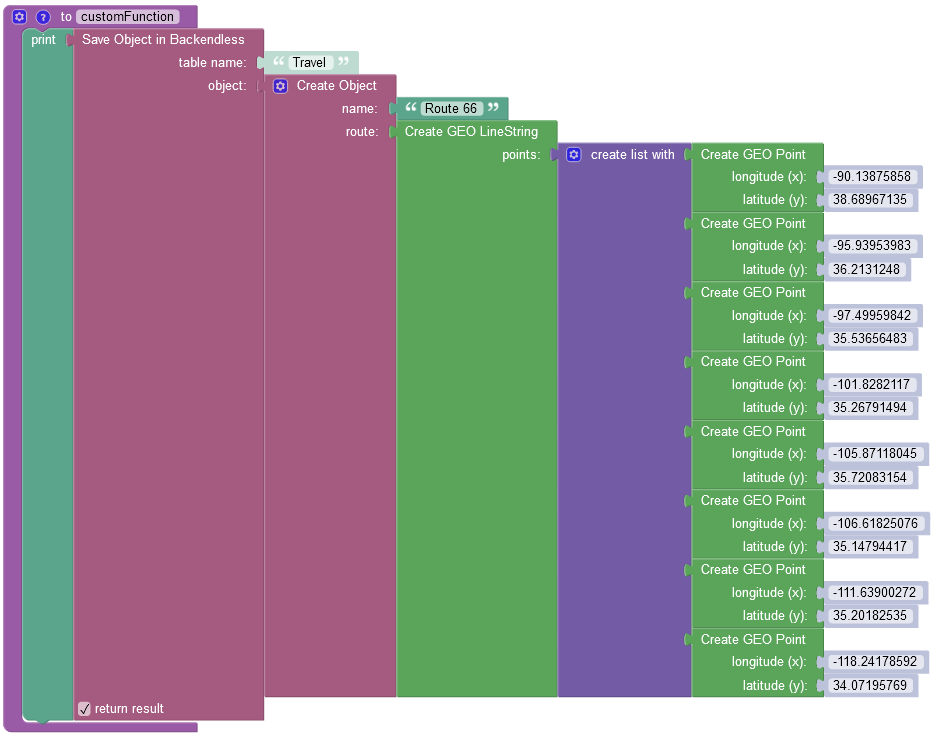
where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
table name |
Name of the data table where a new record must be saved. |
object |
An object to save in the database. Object properties must match the names of the table columns. The object must not have the objectId property. |
return result |
Optional parameter. When this box is checked, the operation returns the saved object with the objectId property. |
When you run the code(or Codeless Logic), you will see the following object in the database:
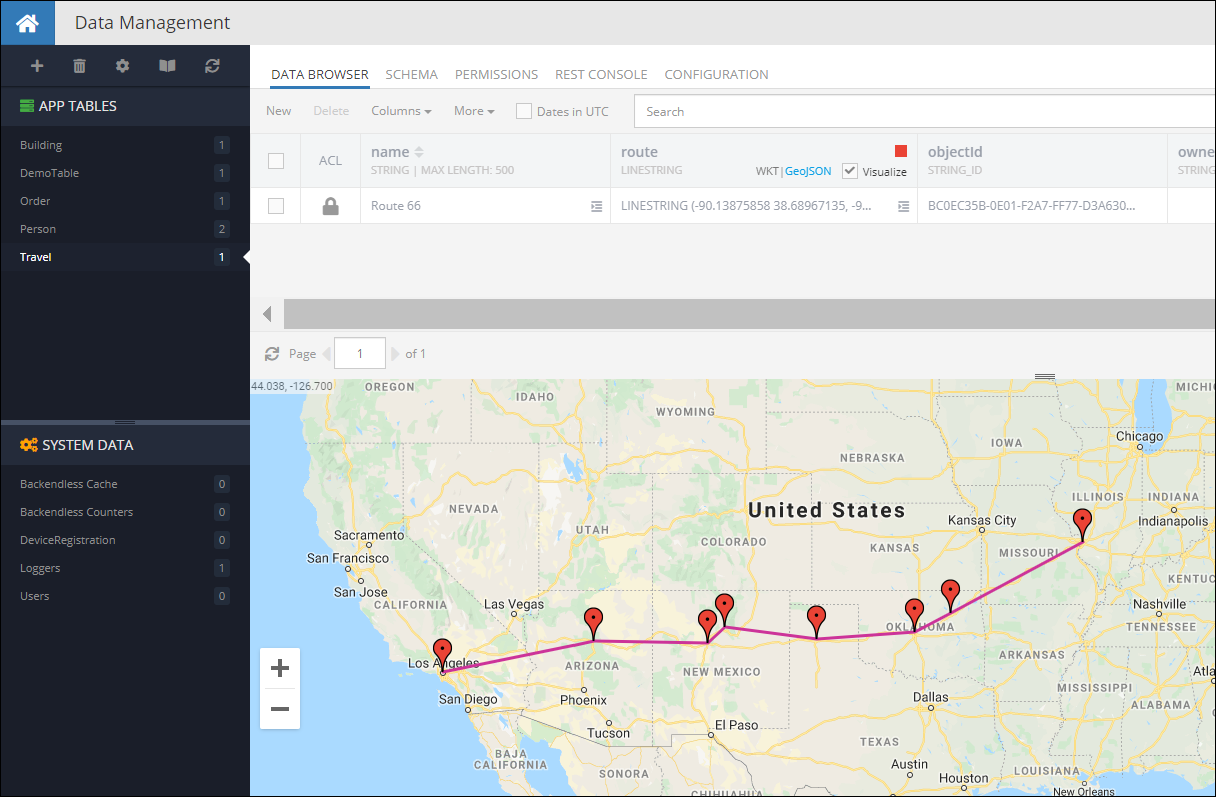
POLYGON Values¶
Creating objects with properties of type POLYGON can be done by using the Backendless.Data.Polygon class. Consider the following example, it is a data table called Building with a schema which includes a column named shape of type POLYGON:
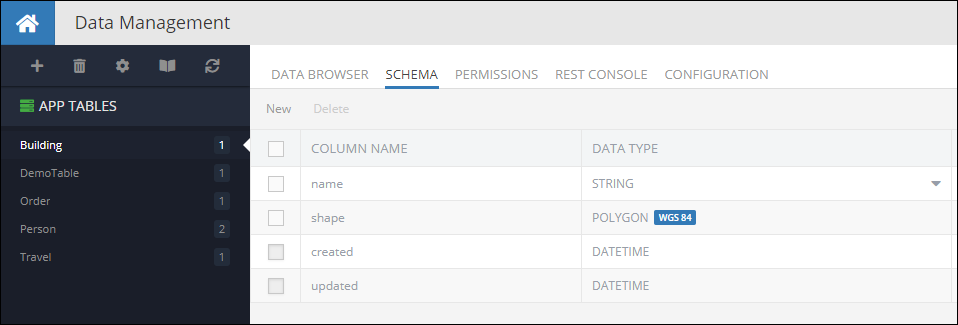
The code below demonstrates how to create a new object with a POLYGON property in the database:
const pentagonPolygonString = 'POLYGON (' +
'(-77.05786152 38.87261877, ' +
'-77.0546978 38.87296123, ' +
'-77.05317431 38.87061405, ' +
'-77.0555883 38.86882611, ' +
'-77.05847435 38.87002898, ' +
'-77.05786152 38.87261877), ' +
'(-77.05579215 38.87026286, ' +
'-77.05491238 38.87087264, ' +
'-77.05544882 38.87170794, ' +
'-77.05669337 38.87156594, ' +
'-77.05684357 38.87072228, ' +
'-77.05579215 38.87026286))'
const pentagonBuildingShape = Backendless.Data.Polygon.fromWKT(pentagonPolygonString)
const buildingObject = {
name : 'Pentagon',
shape: pentagonBuildingShape
}
Backendless.Data.of('Building').save(buildingObject)
.then(savedObject => {
const { objectId } = savedObject
})
.catch(error => {
})
Building class:
class Building {
constructor() {
this.name = null
this.shape = null
this.objectId = null
}
getName() {
return this.name
}
setName(name) {
this.name = name
}
getShape() {
return this.shape
}
setShape(shape) {
this.shape = shape
}
getObjectId() {
return this.objectId
}
setObjectId(objectId) {
this.object = objectId
}
}
const pentagonPolygonString = 'POLYGON (' +
'(-77.05786152 38.87261877, ' +
'-77.0546978 38.87296123, ' +
'-77.05317431 38.87061405, ' +
'-77.0555883 38.86882611, ' +
'-77.05847435 38.87002898, ' +
'-77.05786152 38.87261877), ' +
'(-77.05579215 38.87026286, ' +
'-77.05491238 38.87087264, ' +
'-77.05544882 38.87170794, ' +
'-77.05669337 38.87156594, ' +
'-77.05684357 38.87072228, ' +
'-77.05579215 38.87026286))'
const pentagonBuildingShape = Backendless.Data.Polygon.fromWKT(pentagonPolygonString)
const buildingObject = new Building()
buildingObject.setName('Pentagon')
buildingObject.setShape(pentagonBuildingShape)
Backendless.Data.of(Building).save(buildingObject)
.then(savedObject => {
const objectId = savedObject.getObjectId()
})
.catch(error => {
})
Notice the example above uses the Polygon.fromWKT method to convert a string representation of a geometry into an instance of the Polygon class. Alternatively, the code can use a constructor in the Polygon class which accepts two collections - the boundary points and the holes. The example below and the one above produce exactly the same result using different approaches available in the SDK:
const Point = Backendless.Data.Point
const boundary = []
boundary.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05786152).setLatitude(38.87261877))
boundary.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.0546978).setLatitude(38.87296123))
boundary.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05317431).setLatitude(38.87061405))
boundary.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.0555883).setLatitude(38.86882611))
boundary.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05847435).setLatitude(38.87002898))
boundary.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05786152).setLatitude(38.87261877))
const hole = []
hole.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05579215).setLatitude(38.87026286))
hole.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05491238).setLatitude(38.87087264))
hole.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05544882).setLatitude(38.87170794))
hole.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05669337).setLatitude(38.87156594))
hole.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05684357).setLatitude(38.87072228))
hole.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05579215).setLatitude(38.87026286))
const holes = [new Backendless.Data.LineString(hole)]
const pentagonBuildingShape = new Backendless.Data.Polygon(boundary, holes)
const buildingObject = {
name : 'Pentagon',
shape: pentagonBuildingShape
}
Backendless.Data.of('Building').save(buildingObject)
.then(savedObject => {
const { objectId } = savedObject
})
.catch(error => {
})
Building class:
import com.backendless.persistence.Polygon;
public class Building
{
private String name;
private Polygon shape;
private String objectId;
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public void setName( String name )
{
this.name = name;
}
public Polygon getShape()
{
return shape;
}
public void setShape( Polygon shape )
{
this.shape = shape;
}
public String getObjectId()
{
return objectId;
}
public void setObjectId( String objectId )
{
this.objectId = objectId;
}
}
const Point = Backendless.Data.Point
const boundary = []
boundary.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05786152).setLatitude(38.87261877))
boundary.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.0546978).setLatitude(38.87296123))
boundary.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05317431).setLatitude(38.87061405))
boundary.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.0555883).setLatitude(38.86882611))
boundary.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05847435).setLatitude(38.87002898))
boundary.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05786152).setLatitude(38.87261877))
const hole = []
hole.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05579215).setLatitude(38.87026286))
hole.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05491238).setLatitude(38.87087264))
hole.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05544882).setLatitude(38.87170794))
hole.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05669337).setLatitude(38.87156594))
hole.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05684357).setLatitude(38.87072228))
hole.push(new Point().setLongitude(-77.05579215).setLatitude(38.87026286))
const holes = [new Backendless.Data.LineString(hole)]
const pentagonBuildingShape = new Backendless.Data.Polygon(boundary, holes)
const buildingObject = new Building()
buildingObject.setName('Pentagon')
buildingObject.setShape(pentagonBuildingShape)
Backendless.Data.of(Building).save(buildingObject)
.then(savedObject => {
const objectId = savedObject.getObjectId()
})
.catch(error => {
})
Codeless Reference
The example below creates a new object containing one GeoJSON (Polygon) object and saves it to the database called geolocation:
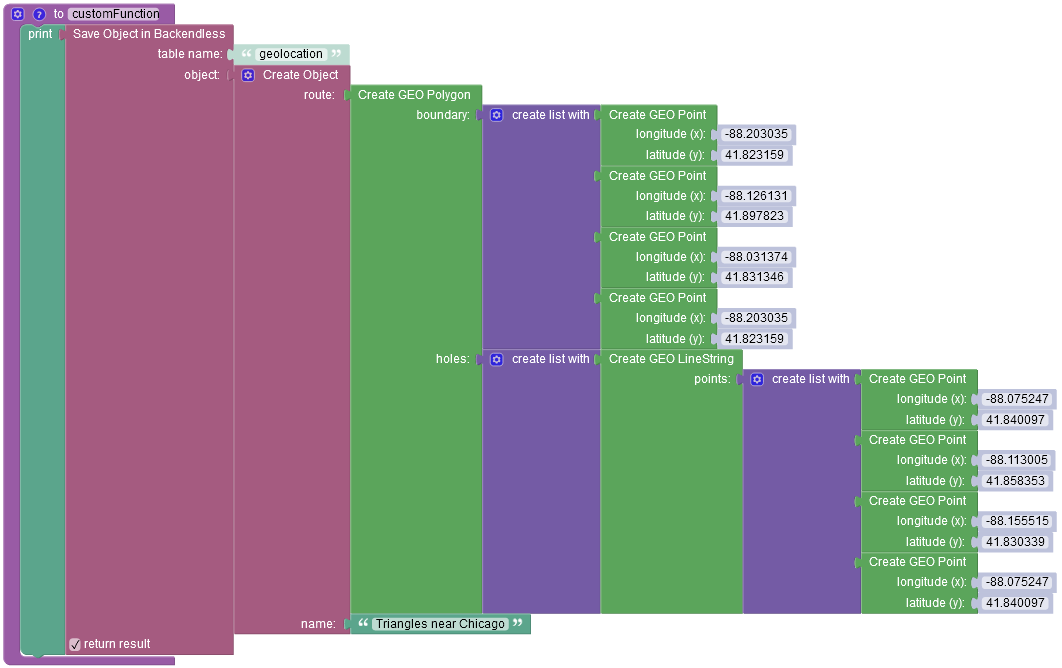
where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
table name |
Name of the data table where a new record must be saved. |
object |
An object to save in the database. Object properties must match the names of the table columns. The object must not have the objectId property. |
return result |
Optional parameter. When this box is checked, the operation returns the saved object with the objectId property. |
After running the code(or Codeless Logic), you will see the following object in the database: