Logic in Layouts¶
Layout Data¶
When working with layouts in Backendless UI Builder, a key feature to understand is the Layout Data data model. This model is essential for managing data across different pages that share the same layout.
What is Layout Data?¶
Layout Data is a special type of data model in UI Builder, similar to App Data and Page Data. However, it differs significantly in its scope and lifecycle.
Scope and Lifecycle¶
- Scope: The scope of
Layout Datais directly tied to the active lifespan of the layout it's associated with. It's not as broad asApp Datanor as limited asPage Data. - Lifecycle: The data within
Layout Datapersists as long as the layout remains active.
Practical Scenario¶
Imagine your app has pages A, B, and C, all using a layout named "Shop". Here's how Layout Data plays a role:
- Data Sharing: Any data placed into the
Layout Databy these pages is accessible across them. - Navigation Impact: As the user navigates between pages A, B, and C, the data in
Layout Dataremains available, regardless of the navigation order. - Layout Change Effect: If the user moves to page D, which either uses a different layout or no layout, the
Layout Datafor the "Shop" layout is cleared.
Implications for App Design¶
This feature of Layout Data provides a powerful tool for developers:
- Consistency in Data: It ensures data consistency across pages sharing the same layout.
- Data Isolation: It provides a mechanism to isolate data relevant only to a specific part of the app journey.
- Dynamic User Experience: Developers can leverage this to create a more dynamic and responsive user experience, where data reacts to user navigation patterns.
Integrating Layout Data in Logic¶
In the practical world of Backendless UI Builder, the concept of Layout Data plays a crucial role in enhancing the dynamic nature of app interfaces. When you embark on programming logic for layouts or pages, the presence of the Layout Data block is immediately noticeable, providing a foundation for complex interactions.
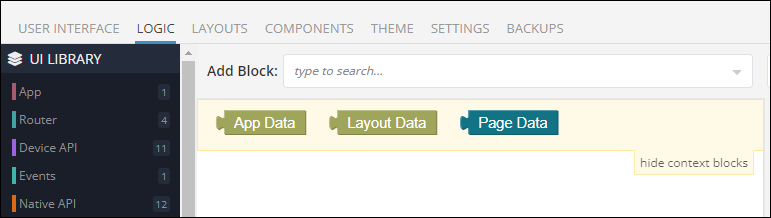
Similarly, data-bindable properties of a layout component reveal an important aspect: the Layout Data Model is the default data model. This integration is key for ensuring seamless interactivity within your app's layout.
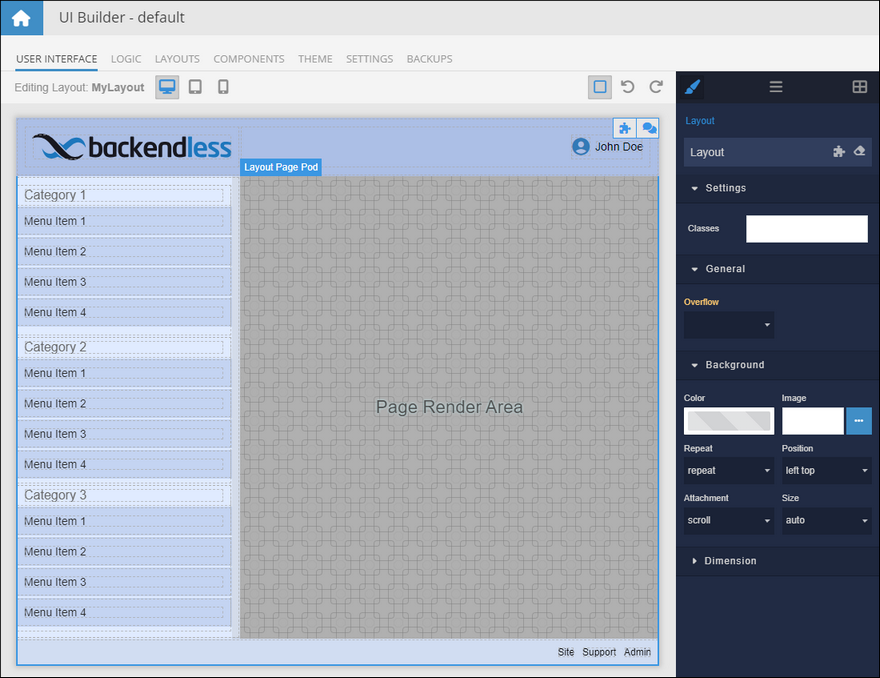
Practical Application: Dynamic Menu Visibility¶
Consider an application interface that includes a header, footer, and a menu. Below is a sample layout that may be applicable to the app:
Suppose that for some pages which use the layout, specific sections of the menu, like the Category 3 block, might need to be dynamically hidden or shown based on the page being viewed. This is where Layout Data's versatility shines. Let’s explore this concept through two example pages: GreenPage and BluePage. Both use the same layout but have different requirements regarding the Category 3 menu item. When GreenPage is active, the Category 3 menu must not be visible, but when BluePage is active, the menu must be visible.
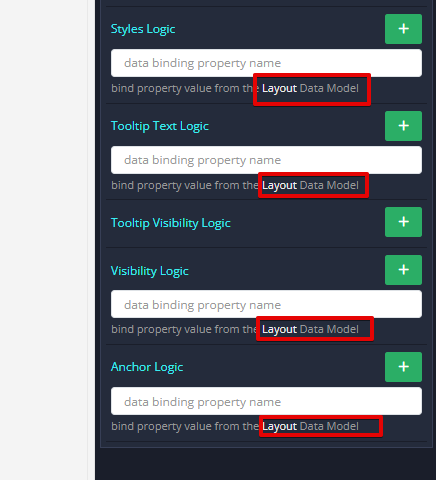
The Category 3 block needs to be configured to have dynamic visibility using the following approach. By establishing a data-binding for the Visibility Logic handler of the menu section, you can effectively control its display. This logic is linked to the showCat3 property within the Layout Data Model, a crucial detail for the ensuing functionality:
Logic for GreenPage¶
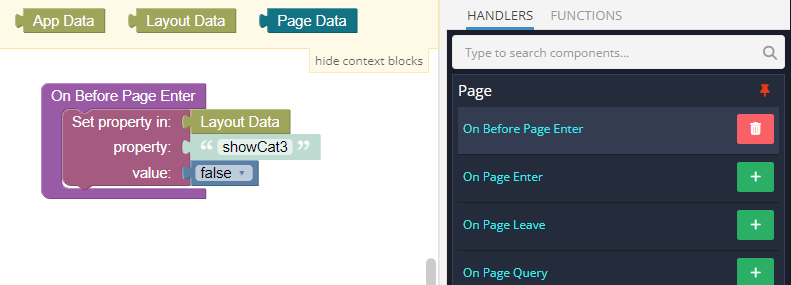
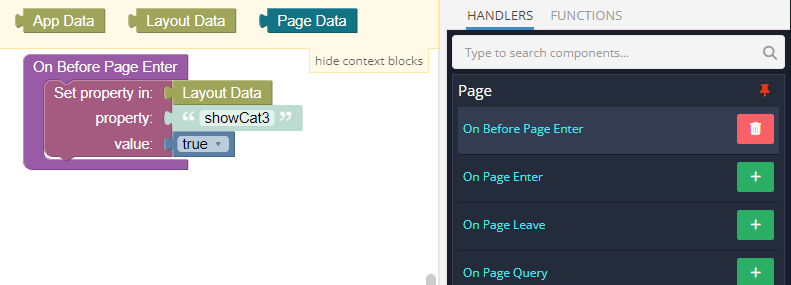
The On Before Page Enter logic of the page is set up to modify the showCat3 property in the Layout Data to false. This action ensures that the Category 3 menu item is hidden when GreenPage is loaded:
Logic for BluePage¶
BluePage, requires a different setup. Its logic is similar to GreenPage's but sets showCat3 to true, making the Category 3 menu item visible when the page is active:
Dynamic Interaction Through Navigation¶
To demonstrate the dynamic nature of this setup, both pages include a navigation button that leads to the other page. This setup allows for a real-time demonstration of how the visibility of the Category 3 menu item in the layout is controlled by the active page.