Upsert Single Object¶
Description¶
With this operation, you can either update an existing object or insert a new one into the database. To update an existing object, the operation locates it using its objectId value. If the object cannot be found, the operation inserts a new object into the data table with the specified objectId value.
Method¶
Blocking API:
// dictionary approach
public Dictionary<String, Object> Backendless.Data.Of( "TABLE-NAME" ).Save( Dictionary<String, Object> dict, Boolean isUpsert = false );
// class approach
public T Backendless.Data.Of<T>().Save( T entity, Boolean isUpsert = false );
Non-blocking API:
// dictionary approach
public Task<Dictionary<String, Object>> Backendless.Data.Of( "TABLE-NAME" ).SaveAsync( Dictionary<String, Object> dict, Boolean isUpsert = false );
// class approach
public Task<T> Backendless.Data.Of<T>().SaveAsync( T entity, Boolean isUpsert = false );
Non-blocking API with Callback:
// dictionary approach
public void Backendless.Data.Of( "TABLE-NAME" ).Save( Dictionary<String, Object> entity,
AsyncCallback<Dictionary<String, Object>> responder,
Boolean isUpsert = false );
// class approach
public void Backendless.Data.Of<T>().Save( T entity,
AsyncCallback<T> responder,
Boolean isUpsert = false );
where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
object |
Required parameter.A dictionary/map which is used for the upsert operation. It must contain the objectId property with the value identifying an existing object or a new object that must be inserted in the data table. |
isUpsert |
Optional parameter. Boolean value. When this property is set to true, the operation tries finding an existing object in the data table to update it. If it can't find the object, it creates (inserts) a new one in the data table. |
"TABLE-NAME" |
Required parameter. String value. Name of the table where the object will be updated/inserted. |
Return Value¶
An object that was updated or inserted into the data table.
Example¶
The example below upserts an object in the "Person" table. It does it by checking if the object with the specified "objectId" already exists. In case it finds the object, it updates it with the new "age" and "email" values. If the object does not exist, the operation inserts a new object into the data table containing the specified "objectId" and the specified property values.
Blocking API:
// dictionary approach
Dictionary<String, Object> entity = new Dictionary<String, Object> { { "objectId", "297BEFCD-2992-4724-8AAC-F3EB00E413D2" }, { "email", "peter@yourmail.com"}, { "age", 55} };
var result = Backendless.Data.Of("Person").Save(entity, true);
// further operations with result
// class approach
Person person = new Person();
person.objectId = "297BEFCD-2992-4724-8AAC-F3EB00E413D2";
person.email = "peter@yourmail.com";
person.age = 55;
var result = Backendless.Data.Of<Person>().Save(person, true);
// further operations with result
Non-blocking API:
// dictionary approach
Dictionary<String, Object> entity = new Dictionary<String, Object> { { "objectId", "297BEFCD-2992-4724-8AAC-F3EB00E413D2" }, { "email", "peter@yourmail.com"}, { "age", 55} };
var result = await Backendless.Data.Of("Person").SaveAsync(entity, true);
// further operations with result
// class approach
Person person = new Person();
person.objectId = "297BEFCD-2992-4724-8AAC-F3EB00E413D2";
person.email = "peter@yourmail.com";
person.age = 55;
var result = await Backendless.Data.Of<Person>().SaveAsync(person, true);
// some work with result
Non-blocking API with Callback:
// dictionary approach
Dictionary<String, Object> entity = new Dictionary<String, Object> { { "objectId", "297BEFCD-2992-4724-8AAC-F3EB00E413D2" }, { "email", "peter@yourmail.com"}, { "age", 55} };
Backendless.Data.Of("Person").Save(entity, new AsyncCallback<Dictionary<String, Object>>(
response =>
{
// operation with result
},
fault=>
{
// error handling logic
}), true);
// class approach
Person person = new Person();
person.objectId = "297BEFCD-2992-4724-8AAC-F3EB00E413D2";
person.email = "peter@yourmail.com";
person.age = 55;
Backendless.Data.Of<Person>().Save(entity, new AsyncCallback<Person>(
response =>
{
// operation with result
},
fault=>
{
// error handling logic
}), true);
Codeless Reference¶

where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
table name |
Name of the data table where the operation must apply changes. |
object |
The object may contain the objectId property identifying an existing object in the database that must be updated, or a new object that must be inserted into the data table. |
return result |
When this box is checked, the operation returns an updated or newly inserted object. |
Returns an object that was updated or inserted into the data table.
Consider the following records in the Person data table:
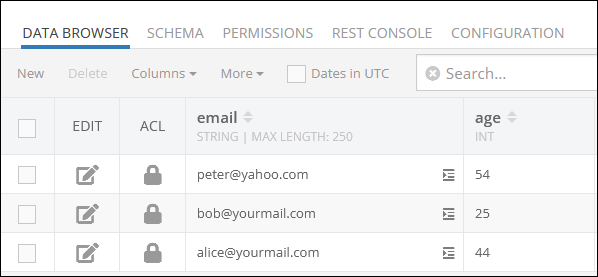
The example below uses the "objectId" value to search the "Person" data table for an object that may exist. In case it finds the object, it just updates it with new "age" and "email" values. If the object does not exist, the operation inserts a new object into the data table containing the specified "objectId" and other values.
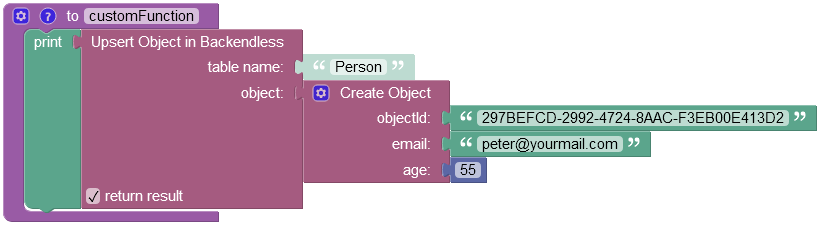
The output will look as shown below after the Codeless logic runs. The value in the "age" column was increased from 54 to 55, and the "email" was changed from "peter@yahoo.com" to "peter@yourmail.com".