MAX¶
The Max aggregate function allows you to retrieve the largest value for a set of objects. To use the function, include Max(columnNameInDatabase) into the list of properties requested from the server. For example, the following query retrieves the largest box office earnings from the Moviesdata table:
DataQueryBuilder queryBuilder = DataQueryBuilder.Create();
queryBuilder.AddProperty( "Max(totalBoxOffice)" );
// ***********************************************************
// Blocking API:
// ***********************************************************
IList<Dictionary<string, object>> result;
result = Backendless.Data.Of( "Movie" ).Find( queryBuilder );
// ***********************************************************
// Non-blocking API:
// ***********************************************************
AsyncCallback<IList<Dictionary<string, object>>> findCallback;
findCallback = new AsyncCallback<IList<Dictionary<string, object>>>(
aggrResult =>
{
// print out the first object from the collection
System.Console.WriteLine( aggrResult[ 0 ] );
},
error =>
{
System.Console.WriteLine( "Server returned an error " + error.Message );
} );
Backendless.Data.Of( "Movie" ).Find( queryBuilder, findCallback );
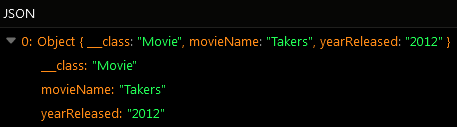
max property in the returned object. The value of the property is the largest amount in the totalBoxOffice column for all movies in the database:
The function can be applied not only to the columns containing numerical values. For example, the following query retrieves the "largest" alphanumeric value for the a movie title:
DataQueryBuilder queryBuilder = DataQueryBuilder.Create();
queryBuilder.AddProperty( "Max(title)" );
// ***********************************************************
// Blocking API:
// ***********************************************************
IList<Dictionary<string, object>> result;
result = Backendless.Data.Of( "Movie" ).Find( queryBuilder );
// ***********************************************************
// Non-blocking API:
// ***********************************************************
AsyncCallback<IList<Dictionary<string, object>>> findCallback;
findCallback = new AsyncCallback<IList<Dictionary<string, object>>>(
aggrResult =>
{
// print out the first object from the collection
System.Console.WriteLine( aggrResult[ 0 ] );
},
error =>
{
System.Console.WriteLine( "Server returned an error " + error.Message );
} );
Backendless.Data.Of( "Movie" ).Find( queryBuilder, findCallback );
Using Alias¶
To change the name of the returned property from min to a custom name, use the following syntax:
Max( columnNameInDatabase ) as customPropertyName
For example, the following query returns the maximum amount in the maximumTotal property:
DataQueryBuilder queryBuilder = DataQueryBuilder.Create();
queryBuilder.AddProperty( "Max(totalBoxOffice) as maxTotal" );
// ***********************************************************
// Blocking API:
// ***********************************************************
IList<Dictionary<string, object>> result;
result = Backendless.Data.Of( "Movie" ).Find( queryBuilder );
// ***********************************************************
// Non-blocking API:
// ***********************************************************
AsyncCallback<IList<Dictionary<string, object>>> findCallback;
findCallback = new AsyncCallback<IList<Dictionary<string, object>>>(
aggrResult =>
{
// print out the first object from the collection
System.Console.WriteLine( aggrResult[ 0 ] );
},
error =>
{
System.Console.WriteLine( "Server returned an error " + error.Message );
} );
Backendless.Data.Of( "Movie" ).Find( queryBuilder, findCallback );
minimumTotal property:
Grouping Results¶
Results in the response can be grouped by values from another column. To request grouping of the results, add the groupBy parameter to the request with the value containing the name of the column. For example, the following request returns the maximum earnings value for the movies in the database grouped by the year the movies were released:
DataQueryBuilder queryBuilder = DataQueryBuilder.Create();
queryBuilder.AddProperty( "Max(totalBoxOffice)" );
queryBuilder.AddProperty( "yearReleased" );
queryBuilder.AddGroupBy( "yearReleased" );
// ***********************************************************
// Blocking API:
// ***********************************************************
IList<Dictionary<string, object>> result;
result = Backendless.Data.Of( "Movie" ).Find( queryBuilder );
// ***********************************************************
// Non-blocking API:
// ***********************************************************
AsyncCallback<IList<Dictionary<string, object>>> findCallback;
findCallback = new AsyncCallback<IList<Dictionary<string, object>>>(
aggrResult =>
{
// print out the first object from the collection
System.Console.WriteLine( aggrResult[ 0 ] );
},
error =>
{
System.Console.WriteLine( "Server returned an error " + error.Message );
} );
Backendless.Data.Of( "Movie" ).Find( queryBuilder, findCallback );
Sorting¶
The results can be sorted using the sortBy parameter. For example, results for the following request will be sorted by the values in the yearReleased column in the descending order:
DataQueryBuilder queryBuilder = DataQueryBuilder.Create();
queryBuilder.AddProperty( "Max(totalBoxOffice)" );
queryBuilder.AddProperty( "yearReleased" );
queryBuilder.AddSortBy( "yearReleased DESC" );
// ***********************************************************
// Blocking API:
// ***********************************************************
IList<Dictionary<string, object>> result;
result = Backendless.Data.Of( "Movie" ).Find( queryBuilder );
// ***********************************************************
// Non-blocking API:
// ***********************************************************
AsyncCallback<IList<Dictionary<string, object>>> findCallback;
findCallback = new AsyncCallback<IList<Dictionary<string, object>>>(
aggrResult =>
{
// print out the first object from the collection
System.Console.WriteLine( aggrResult[ 0 ] );
},
error =>
{
System.Console.WriteLine( "Server returned an error " + error.Message );
} );
Backendless.Data.Of( "Movie" ).Find( queryBuilder, findCallback );
DataQueryBuilder queryBuilder = DataQueryBuilder.Create();
queryBuilder.AddProperty( "Max(totalBoxOffice) as maxTotal" );
queryBuilder.AddProperty( "yearReleased" );
queryBuilder.AddSortBy( "maxTotal" );
// ***********************************************************
// Blocking API:
// ***********************************************************
IList<Dictionary<string, object>> result;
result = Backendless.Data.Of( "Movie" ).Find( queryBuilder );
// ***********************************************************
// Non-blocking API:
// ***********************************************************
AsyncCallback<IList<Dictionary<string, object>>> findCallback;
findCallback = new AsyncCallback<IList<Dictionary<string, object>>>(
aggrResult =>
{
// print out the first object from the collection
System.Console.WriteLine( aggrResult[ 0 ] );
},
error =>
{
System.Console.WriteLine( "Server returned an error " + error.Message );
} );
Backendless.Data.Of( "Movie" ).Find( queryBuilder, findCallback );
Codeless Reference¶
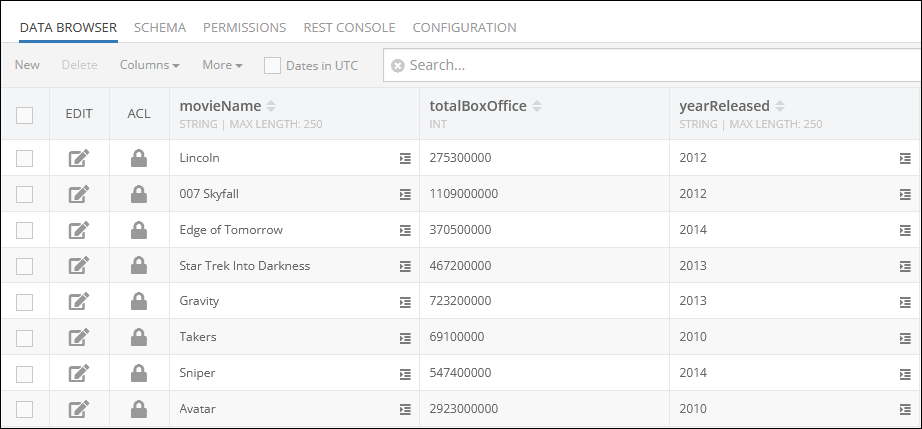
Consider the following data table called Movie:
The example below extracts the greatest value from the totalBoxOffice column. To retrieve the greatest value you must use the aggregate function Max(columnName) in the properties argument:
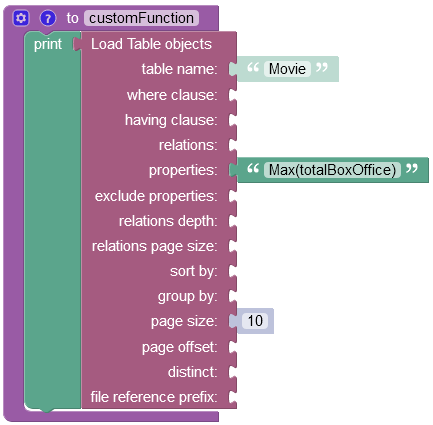
Important
For a detailed description of all input parameters see the Basic Object Retrieval topic of this guide.
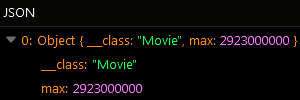
After the Codeless logic runs the operation returns an object with the max property containing the value which reflects the greatest of all values stored in the requested column/property:
Using Alias¶
Any default property returned in the response can have a custom name. You can change the default property name (e.g. max) returned in the response by defining a dynamic property as shown in the excerpt below. The totalBoxOffice is the name of the column in the data table, and the greatestBoxOffice is the custom property name that will be shown in the response instead of the current property name (e.g. max):
Max(totalBoxOffice) as greatestBoxOffice
The example below retrieves the greatest value stored in the "totalBoxOffice" column and returns the result with a custom property name "greatestBoxOffice":
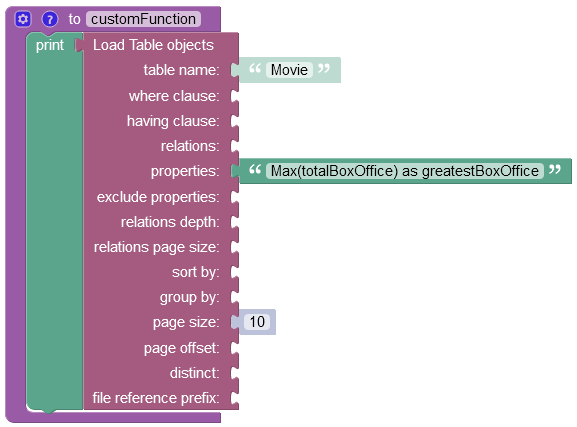
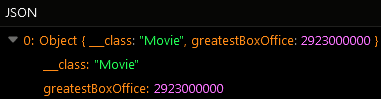
After the Codeless logic runs, the operation returns an object with a new property name greatestBoxOffice:
Grouping The Results¶
Results can be grouped by values from another column. To group results you have to reference the name of the column in the group by property. By doing so, you instruct the operation to create an object for every group of values retrieved from the column referenced in the group by property.
As you reference the column name in the group by property, the operation groups all values first into separate objects, and then it finds the greatest of all values.
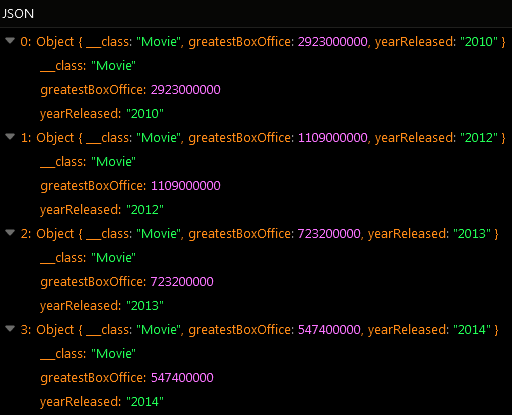
The example below groups values in the totalBoxOffice column by values in the yearReleased column into distinct objects and then finds the greatest value. For better perception of the operation result you can also include the yearReleased column in the properties argument, so that you could see the greatest box office earnings for every year in the response.
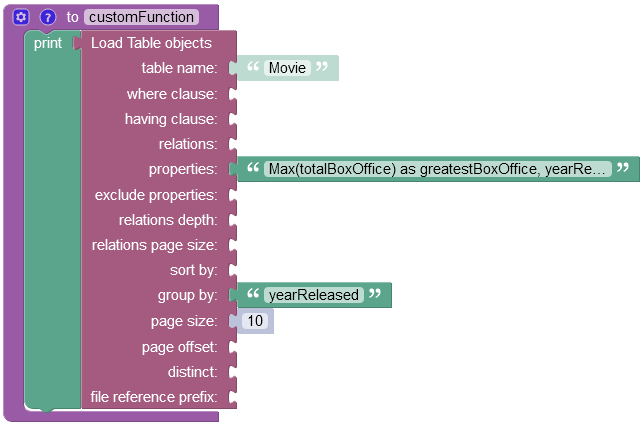
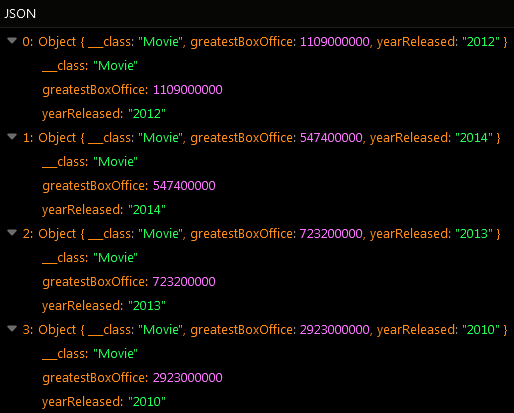
First, the operation has grouped all records into distinct objects based on the values in the yearReleased column passed to the group by property. Then for every object the operation has returned the greatest of all values stored in the totalBoxOffice column.
Sorting¶
You can sort the data by referencing the column name in the sort by property.
Results for the following request will be sorted by the values in the yearReleased column in the descending order:
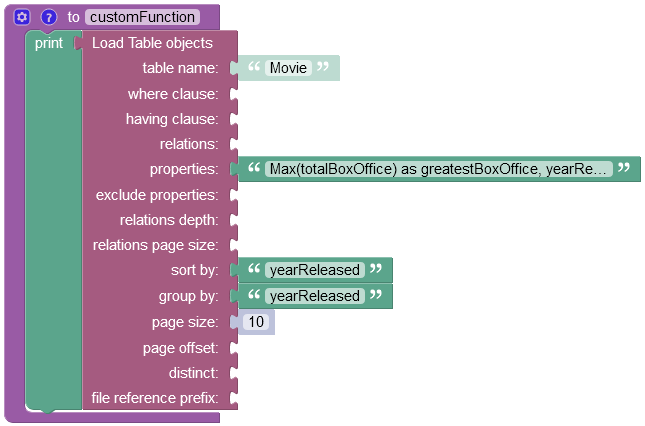
As you can see, objects returned in the response are sorted in descending order by values in the yearReleased column/property:
The function can be applied not only to the columns containing numerical values. For example, the following query retrieves the "largest" alphanumeric value for a movie title:
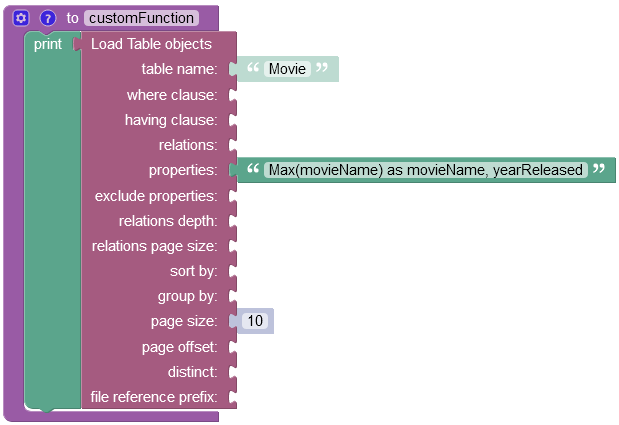
After the Codeless Logic runs, the operation returns an object containing the movieName custom property and the corresponding "largest" alphanumerical value which is "Takers".