Search with SubQuery¶
Search with subquery allows your apps to run two queries in the context of a single data retrieval request. The first query identifies a set of objects which is fed into the second query. Consider the following data schema:
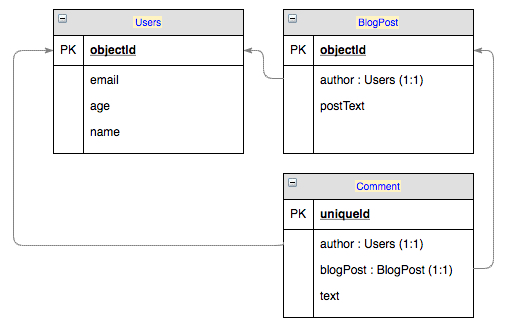
Suppose your app needs to get all blog posts where the person who posted a comment has a specific email address (for example, @backendless.com ). Using subqueries, it can be done with the following whereClause sent to the BlogPost table:
objectId in (Comment[author.email LIKE '%@backendless.com'].blogPost.objectId)
Let's review how this whereClause is processed by Backendless:
- Backendless detects that the query at the top level uses the
in()operator. - It checks if the contents of the
in()operator have the format of a subquery and if so, evaluates it accordingly. - The subquery contains an "internal whereClause", which is:
author.email LIKE '%@backendless.com' - The internal whereClause is applied to the objects in the
Commenttable. - For all found
Commentobjects, Backendless gets a list of values for the blogPost.objectId column. - The resulting set is fed into the
in()operator which fetches the final set of objects from theBlogPosttable.
General SubQuery Syntax¶
The general syntax for subqueries is:
searchColumnNameOrRelatedColumnName IN
(TableName[internalWhereClause].columnOrRelatedColumnName.optionalcolumnName)
How it works:
- If
internalWhereClauseis present, it is executed in the table identified byTableName. - In the resulting set of records, values must be selected for the column identified by
columnOrRelatedColumnName.optionalColumnName. - If
internalWhereClauseis not present, the contents of theINoperator have the following syntax. It represents the entire set of values identified by the specified column:TableName.columnOrRelatedColumnName.optionalColumnName - The resulting set of values is used in the
INoperator, thus the final query ends up being:searchColumnOrRelatedColumnName IN ( value1, value2,,,valueN )
Additional Examples¶
Consider the following data schema:
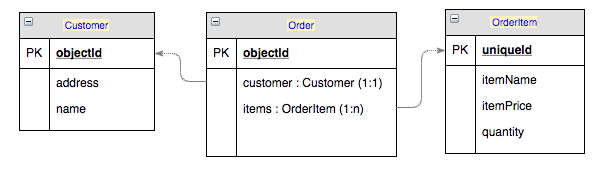
- Get all
OrderItemobjects for a customer fromNew York:objectId in (Order[customer.address = 'New York'].items.objectId) - Get all
Customerobjects who spent more than1.99on an item:objectId in (Order[items.itemPrice > 1.99].customer.objectId)