Reset counter value¶
Resets the current counter value to zero..
// *******************************************
// synchronous methods
// *******************************************
// Backendless.Counters approach
public void Backendless.Counters.reset( String counterName );
// IAtomic approach
IAtomic<T> counter = Backendless.Counters.of( String counterName,
Class<? extends T> type );
public void counter.reset();
// *******************************************
// asynchronous methods
// *******************************************
// Backendless.Counters approach
public void Backendless.Counters.reset( String counterName,
AsyncCallback callback );
// IAtomic approach
IAtomic<T> counter = Backendless.Counters.of( String counterName,
Class<? extends T> type );
public void counter.reset( AsyncCallback callback );
where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
counterName |
name of the counter to reset. |
callback |
the callback used for asynchronous calls to indicate that the operation has either successfully completed or resulted in error. |
Example¶
AsyncCallback callback = new AsyncCallback()
{
@Override
public void handleResponse( Object value )
{
Log.i( "MYAPP", "[ASYNC] counter has been reset" );
}
@Override
public void handleFault( BackendlessFault backendlessFault )
{
Log.e( "MYAPP", "Error - " + backendlessFault.getMessage() );
}
};
Backendless.Counters.reset( "my counter", callback );
IAtomic<Integer> myCounter = Backendless.Counters.of( "my counter", Integer.class );
myCounter.reset();
Log.i( "MYAPP", "[SYNC] counter has been reset" );
Codeless Reference¶

where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
counter name |
Name of the counter whose value must be set to 0. |
This operation does not return a value.
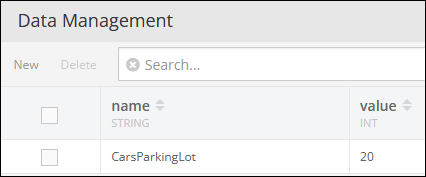
Consider the following counter:
The example below resets the value of the "CarsParkingLot" counter 0.
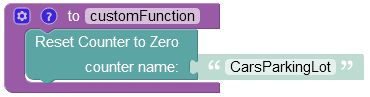
The result of this operation will look as shown below after the Codeless logic runs: