Data retrieval with Sorting¶
Data retrieval and search API can request the server to return sorted data. Data can be sorted by one or more columns. The sorting direction can be either ascending (default) or descending for each individual column. Android applications must use the DataQueryBuilder class to set the sorting option. The example below configures DataQueryBuilder to sort results by the name and age columns. Value in the age column are sorted in the descending order. The query is used to retrieve objects from the Person table:
DataQueryBuilder queryBuilder = DataQueryBuilder.create();
queryBuilder.setSortBy( "name", "age DESC" );
Backendless.Data.of( "Person" ).find( queryBuilder,
new AsyncCallback<List<Map>>()
{
@Override
public void handleResponse( List<Map> response )
{
// the "response" object is a collection of java.util.Map objects.
// each item in the collection represents an object from the "Person" table
}
@Override
public void handleFault( BackendlessFault fault )
{
// use the getCode(), getMessage() or getDetail() on the fault object
// to see the details of the error
}
});
DataQueryBuilder queryBuilder = DataQueryBuilder.create();
queryBuilder.setSortBy( "name", "age DESC" );
Backendless.Data.of( Person.class ).find( queryBuilder,
new AsyncCallback<List<Person>>()
{
@Override
public void handleResponse( List<Person> response )
{
// the "response" object is a collection of Person objects.
// each item in the collection represents an object from the "Person" table
}
@Override
public void handleFault( BackendlessFault fault )
{
// use the getCode(), getMessage() or getDetail() on the fault object
// to see the details of the error
}
});
Important
The descending sorting order can be requested by adding DESC to the name of the column (separated by space).
Codeless Reference¶
Consider the following data table called Movie:
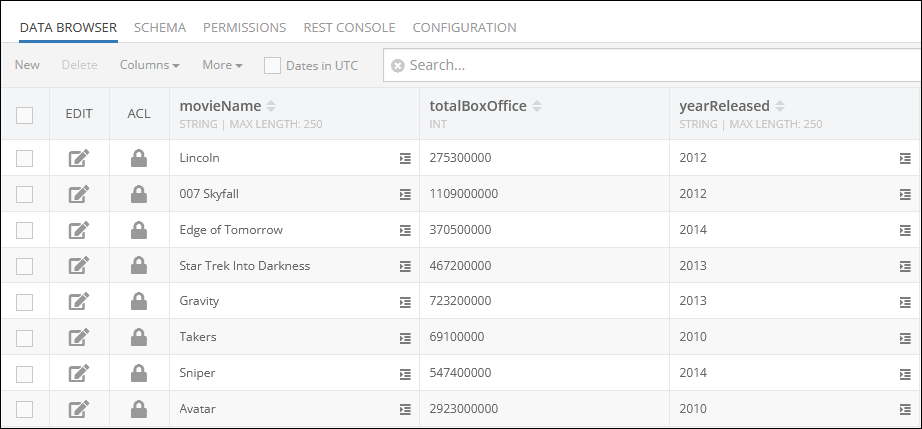
Suppose you need to retrieve records from the data table, but you want to have them sorted in the response by values in a specific column. To do that, you need to reference the name of the column in the sort by property.
The example below retrieves records from the data table and sorts them by values stored in the totalBoxOffice column.
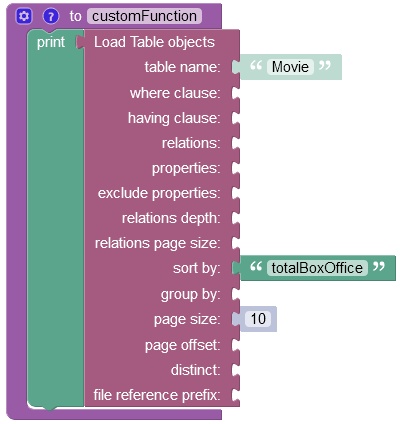
Important
For a detailed description of all input parameters see the Basic Object Retrieval topic of this guide.
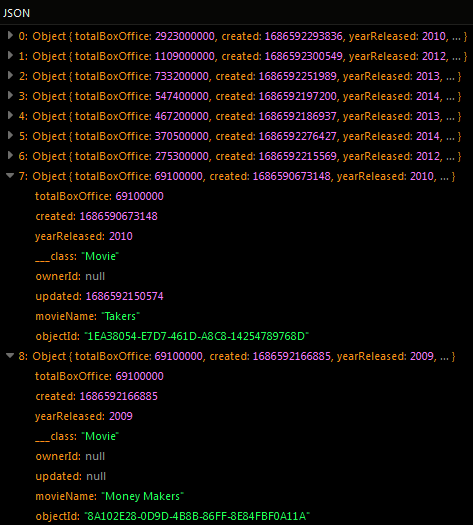
The result of this operation is eight objects sorted by values in the totalBoxOffice property:
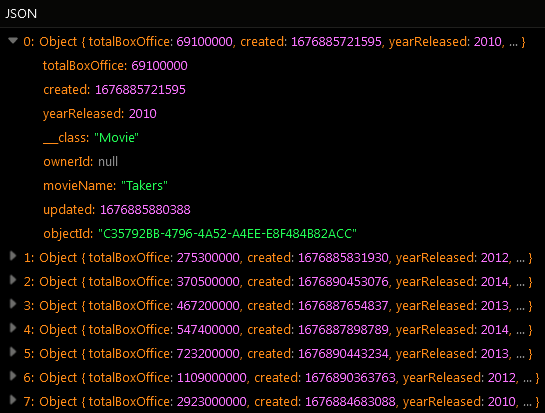
You can also perform double sorting of records by referencing the second column name in the sort by property. The double sorting works only if there are two or more similar values stored in the first column. Once the operation runs, it sorts all values by the first column name and then it sorts values by the second column name.
For demonstration purposes, the data table presented below contains two similar records:
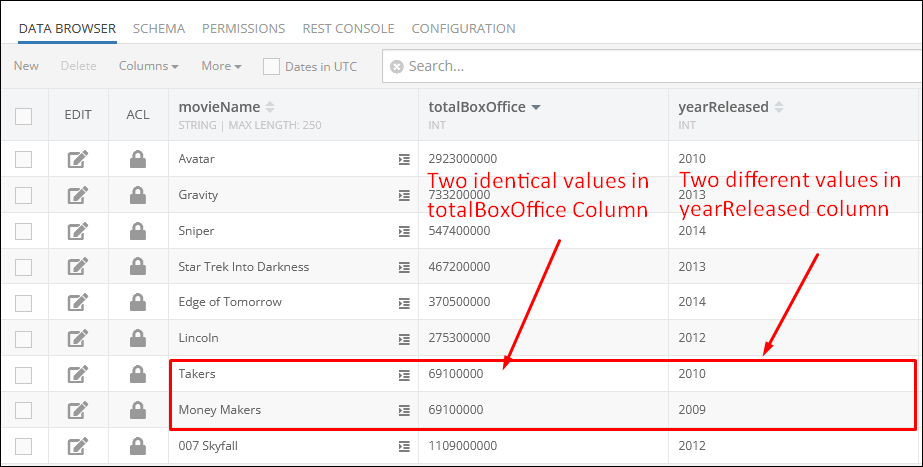
The example below retrieves records from the data table and sorts them by values stored in two columns: totalBoxOffice and yearReleased. It uses an additional argument in the sort by property called "desc" that instructs the operation to sort values in descending order. The ascending order is represented as the "asc" argument.
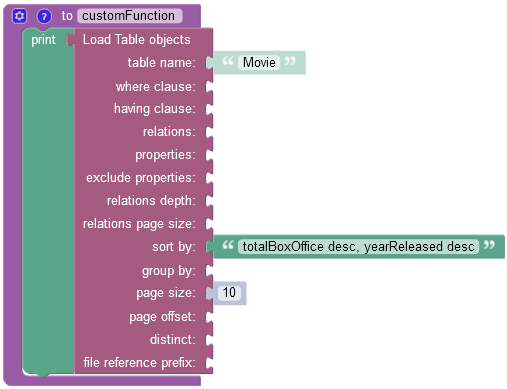
After the Codeless Logic runs, the operation returns objects from the data table sorted by both columns referenced in the sort by property. As you can see, two objects with the smallest values in the "totalBoxOffice" column returned in the response were sorted by both columns, while all other objects were practically sorted only by the first column. It was sorted in this way because the operation considers the first column name referenced in the sort by property as the primary, which forces the operation to find similar or identical values in the specified column first, and then if it sorts similar or identical values in the second column.