Database Functions¶
Backendless Database supports a variety of functions that can perform database data transformations, used for conditions and retrieval of custom properties. Functions can be used in three places:
Consider the following Person data table:
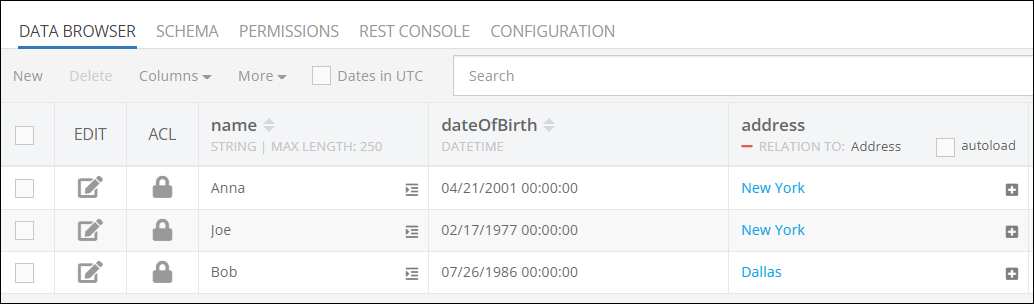
Suppose we need to retrieve records from this table and perform the following:
- Calculate each person's age.
- Convert the name to upper case.
Using functions these tasks can be performed by Backendless instead your program. Below is an example of applying functions to achieve the result. Notice the values in the response:
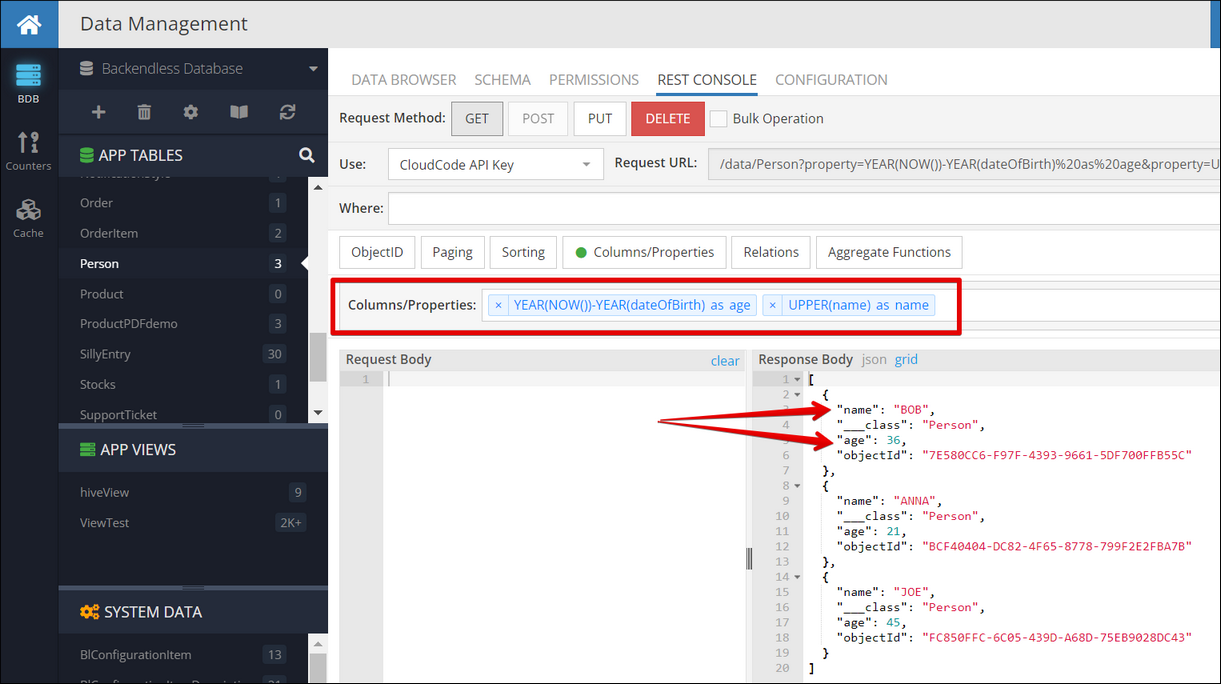
This example uses the following functions:
| Function |
Description |
|---|---|
UPPER(name) |
Converts the value in the name column to upper case |
YEAR(NOW())-YEAR(dateOfBirth) |
Calculates the difference between the current year and the year in the dateOfBirth column. |
Below is an example of using these functions in a Codeless block to retrieve database records:
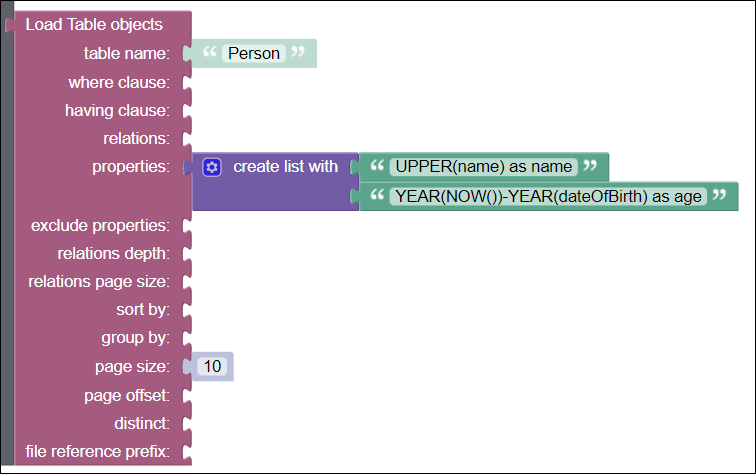
As you case see, functions can be a powerful instrument to offload some data conversions and calculations to the database. Below is a list of functions supported by Backendless:
DATETIME Functions¶
These functions apply to database columns and values of the DATETIME type:
| Function |
Description |
|---|---|
NOW() |
Returns current date/time. The returned value can be used in all functions listed below. Additionally, you can pass the optional fsp ( fractional seconds precision ) argument to the function, that will return a value in the following format: 'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.FFFFFF’ or '2020-06-23 11:19:06.095048'. Note, that the fsp argument returns up to 6 digits of microseconds precision. |
UNIXTIMESTAMP( date ) |
Returns the number of seconds that has passed since 1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC as an unsigned integer. When the date argument is passed to the function, it returns the value of the argument as seconds passed since 1970-01-01 00:00:00 UTC.The date argument can be any of the following:- Name of a database column of the DATETIME type;- A function that returns a date ( DATE(), NOW(), DATEADD(), DATESUB());- Literal date value as a string expressed in any of the supported formats; |
DATEDIFF( date_1, date_2) |
Returns the difference between two values representing the date passed to the function, or in other words this method subtracts date_1 from date_2,and the remainder of this calculation is a date. If one of the values passed to the function is NULL, then NULL is returned. The date argument can be one of the following: DATETIME column, dates, and date-and-time expressions.The example below will return the difference between the actual date '2022/01/01'and the DATETIME column db_date_column_1:DATEDIFF('2022/01/01', db_date_column_1) |
DATE( dateValue or dateTimeColumnName ) |
Extracts the date part of a DATETIME column value. |
TIME( dateValue or dateTimeColumnName ) |
Extracts the time portion of a DATETIME column value. |
WEEK( dateValue or dateTimeColumnName ) |
Returns the week number of a DATETIME column value. |
WEEK( dateValue or dateTimeColumnName, mode ) |
Same as above, but allows you to specify whether the week starts on Sunday or Monday and whether the return value should be in the range from 0 to 53 or from 1 to 53. Second argument mode == 0 ~ 7. The mode argument is: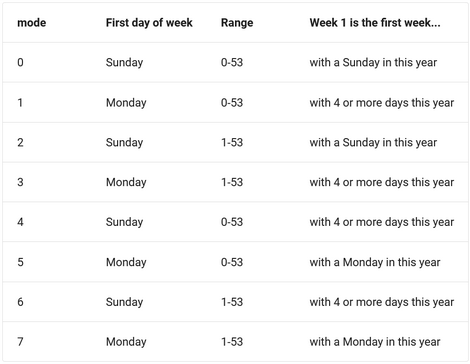 |
MONTH( dateValue or dateTimeColumnName ) |
Returns the month for a DATETIME column value, in the range 1 to 12 for January to December, or 0 for dates such as ‘0000-00-00’. |
QUARTER( dateValue or dateTimeColumnName ) |
Returns the quarter of the year for a DATETIME column value, in the range 1 to 4. |
YEAR( dateValue or dateTimeColumnName ) |
Returns the year for a DATETIME column value, in the range 1000 to 9999, or 0 for the “zero” date. |
DAYOFMONTH( dateValue or dateTimeColumnName ) |
Returns the day of the month for a DATETIME column value, in the range 1 to 31, or 0 for dates such as ‘0000-00-00’. |
DAYOFWEEK( dateValue or dateTimeColumnName ) |
Returns the weekday index for date (1 = Sunday, 2 = Monday, …, 7 = Saturday) |
DAYOFYEAR( dateValue or dateTimeColumnName ) |
Returns the day of the year (1-366) |
HOUR( dateValue or dateTimeColumnName ) |
Returns the hour for time. The range of the return value is 0 to 23 for time-of-day values. |
MINUTE( dateValue or dateTimeColumnName ) |
Returns the minute for time, in the range 0 to 59. |
SECOND( dateValue or dateTimeColumnName ) |
Returns the second for time, in the range 0 to 59. |
DATESUB( dateValue or dateTimeColumnName, intervalValue, intervalName )DATEADD( date, intervalValue, intervalName ) |
Perform arithmetic functions with date values. DATESUB subtracts intervalValue from date. DATEADD adds intervalValue to date.The intervalValue and intervalName arguments must correspond with the values and samples shown below: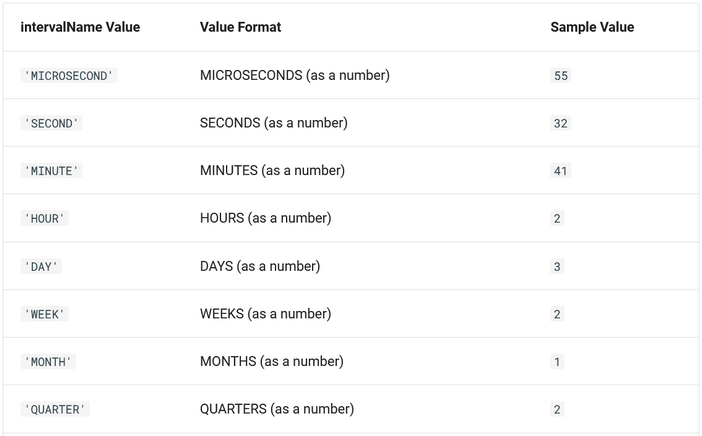 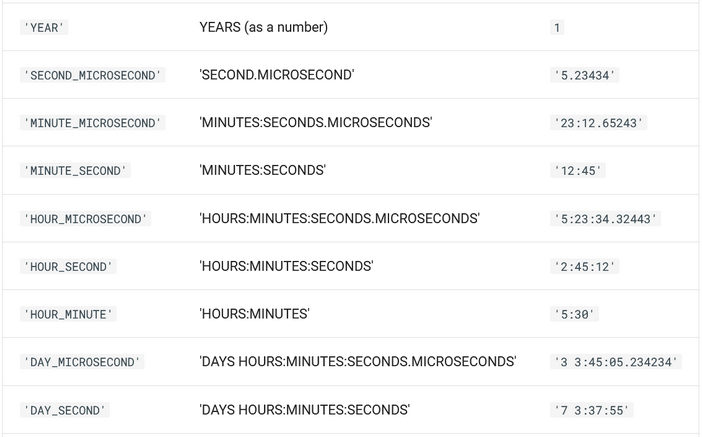 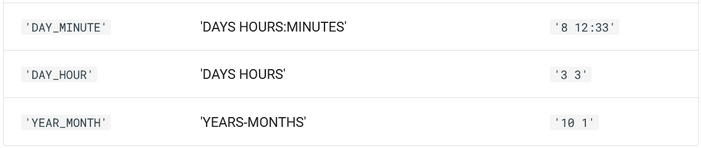 |
STRING Functions¶
These functions apply to database columns and value of the STRING and TEXT type.
| Function |
Description |
|---|---|
TRIM( stringORTextColumnName ) |
Returns a string value from the STRING and TEXT column with leading and trailing spaces removed. |
REVERSE( stringORTextColumnName ) |
Returns a string value with the characters positioned in the reversed order. |
UPPER( stringORTextColumnName ) |
Returns a string value with all alphabetical characters converted to the upper case equivalent. |
LOWER( stringORTextColumnName ) |
Returns a string value with all alphabetical characters converted to the lower case equivalent. |
FINDINSET( stringColumn or stringLiteral, stringColumn or stringLiteral ) |
Finds and returns the position of the value represented by the first argument in a set identified by the second argument. The second argument must be a comma-separated list of strings to be searched. If the second argument is a column name, the search occurs in the values represented by the column. The function returns: - zero if the first argument value is not found in the set identified by the second argument or if the second argument value is an empty string; - a positive integer if the first argument value is found in the second argument's list of strings. The integer is the position in the list. - NULL if either argument is NULL. |
Miscellaneous Functions¶
| Function |
Description |
|---|---|
IF( condition, true_value, false_value ) |
Function allows validating a specific condition. When condition evaluates to true, then true_valueis returned. Otherwise, the false_value is returned. Function arguments can be string, integer or column names. Returned values can be integer or string.WHERE, GROUP BY clauses can be used to make a query: Example 1: curl -X GET 'https://eu-api.backendless.com/:appId/:restKey/data/Person?where=IF(age>18, current_city, birth_city)='New York'Example 2: curl -X GET 'https://eu-api.backendless.com/:appId/:restKey/data/Person?where=IF(age>18, current_city, birth_city)='New York'&property=IF(age>18, 'adult', 'child') as maturity&having=IF(oldIdentityField is null, newIdentityField, oldIdentityField)=1'Example 3: curl -X GET 'https://eu-api.backendless.com/:appId/:restKey/data/Person?property=IF(Bool is not null, true, false)'Example 4: curl -X GET 'https://eu-api.backendless.com/:appId/:restKey/data/Person?property=objectId&property=Age&property=Name&property=Count(objectId)&groupBy=Age&having=if(Age=10, 20, 30) >20'Example 5: curl -X GET 'https://eu-api.backendless.com/:appId/:restKey/data/Person?property=IF(relation.Name like 'A%', Name, Age)'Example 6: curl -X GET 'https://eu-api.backendless.com/:appId/:restKey/data/Person?property=IF(relation.Name like 'A%', upper (Name), date(created)) as 'example''Example 7: curl -X GET 'https://eu-api.backendless.com/:appId/:restKey/data/Person?property= IF(Age > 10, relation.Name, relation.email) as function' |
ISNULL( columnName ) |
Returns 1 if the value in the referenced column is NULL, otherwise returns 0. |
ISNOTNULL( columnName ) |
Returns 1 if the value in the referenced column contains a non-NULL value otherwise returns 0. |
COALESCE( value1, value2, value3, valueN ) |
Function returns the first non-NULL value of a list, or NULL if there are no non-NULL value. |
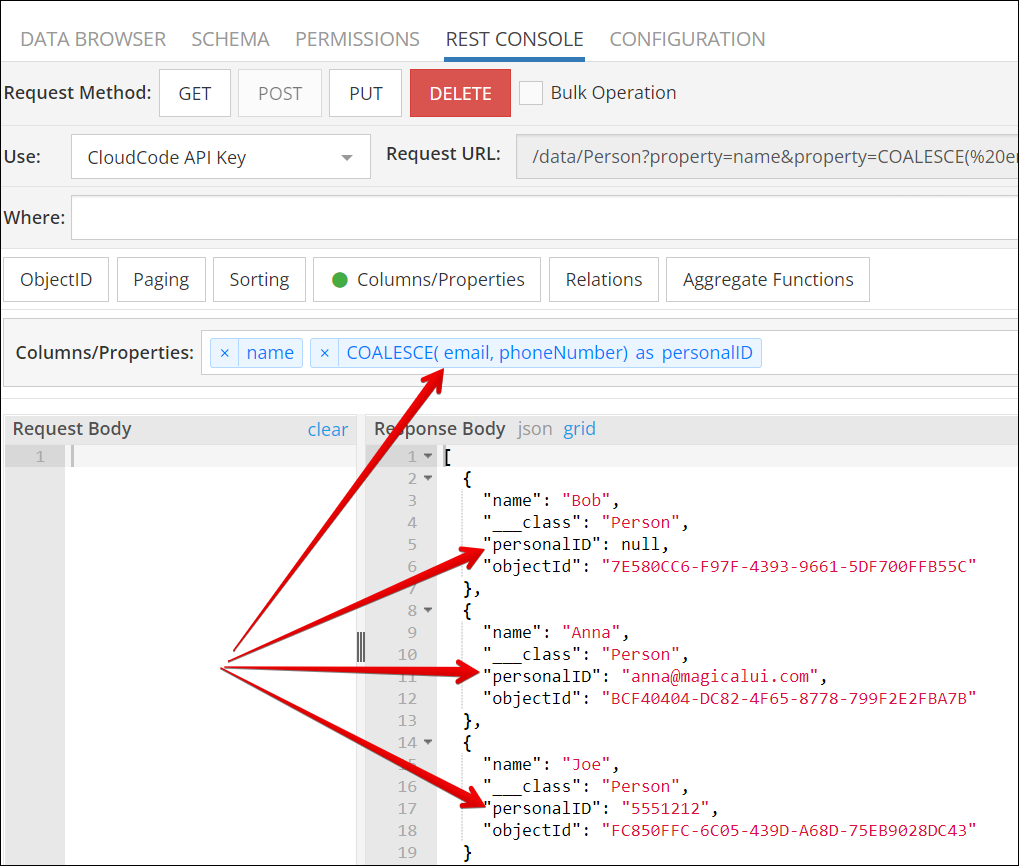
Function arguments can be literal values or column names. When the argument values are column names, the function will return the first non-NULL value from the referenced columns. Consider the following data table. Notice that some records do not have values for the email and phoneNumber columns: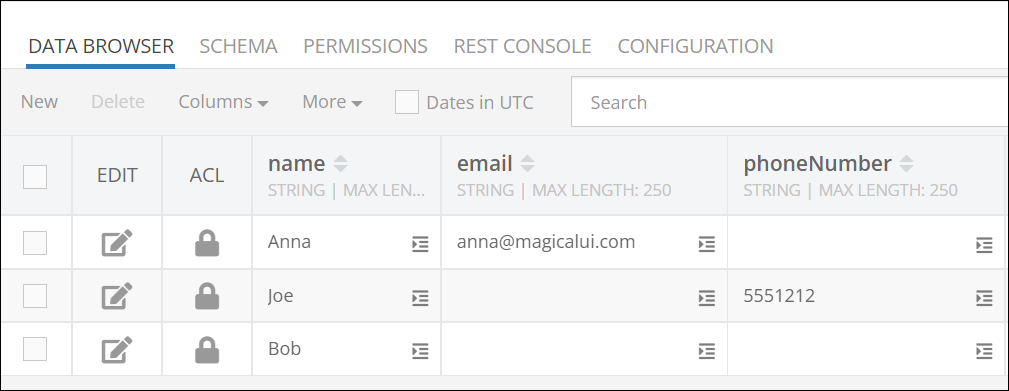
Below is a result of using the COALESCE function to retrieve a non-NULL value from email and phoneNumber columns. As you can see, the function returned:
- NULL for Bob
- a value from the phoneNumbercolumn for Anna
- a value from the email column for Joe