Update with Adding a Relation¶
The Deep Save API can be used to update an existing object and set a relation with a new child (or parent). Consider the examples below:
Existing Parent and New Child¶
This example retrieves an existing parent object (Order) and uses the Deep Save API to perform the following:
- Save new child object (
OrderItem) - Establish relationship between the
Orderand the newOrderItem.
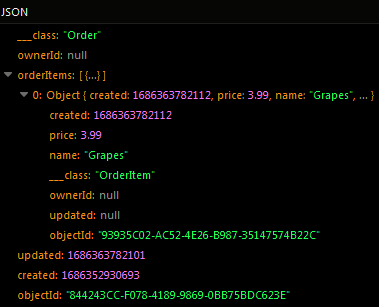
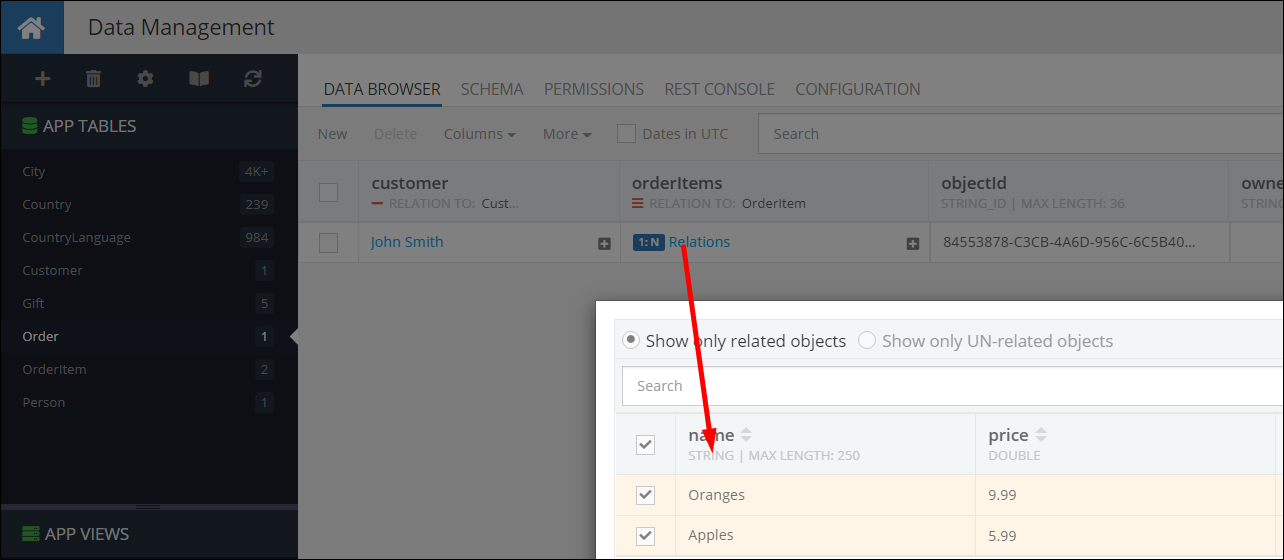
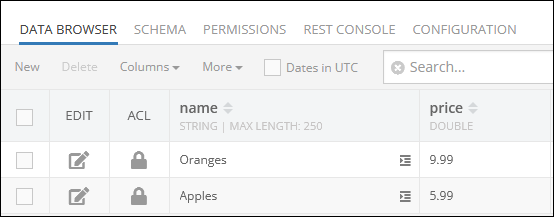
The Order object already has two related OrderItem objects before the sample code below runs:
Important
When working with relationships, the Deep Save API applies the "accumulation" policy. This means the following: if a parent object in the database already has some related objects and you update the object with new child objects in the relation, these objects will be added to the relation.
The example uses blocking API for code brevity. When using in an Android application, keep in mind the blocking API cannot be used on the mail UI thread. Either run it in a separate thread or use the non-blocking API.
// get the order with the relations.
Map<String, Object> order = Backendless.Data.of( "Order" ).findFirst();
// create new order item
Map grapes = new HashMap();
grapes.put( "name", "Grapes" );
grapes.put( "price", 3.99 );
List<Map> orderItems = new ArrayList<>();
// add grapes to the existing order items on the server
orderItems.add( grapes );
// put the list with grapes added to it back into order
order.put( "orderItems", orderItems );
// deep save the order
Backendless.Data.of( "Order" ).deepSave( order );
// get the order object.
Order order = Backendless.Data.of( Order.class ).findFirst();
// create new order item
OrderItem grapes = new OrderItem();
grapes.name = "Grapes";
grapes.price = 3.99;
// add new order item to the existing ones
order.addItem( grapes );
// deep save the order
Backendless.Data.of( Order.class ).deepSave( order );
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Order
{
public String objectId;
public Customer customer;
public ArrayList<OrderItem> orderItems;
public void addItem( OrderItem item )
{
if( orderItems == null )
orderItems = new ArrayList<>();
orderItems.add( item );
}
}
public class OrderItem
{
public String name;
public double price;
}
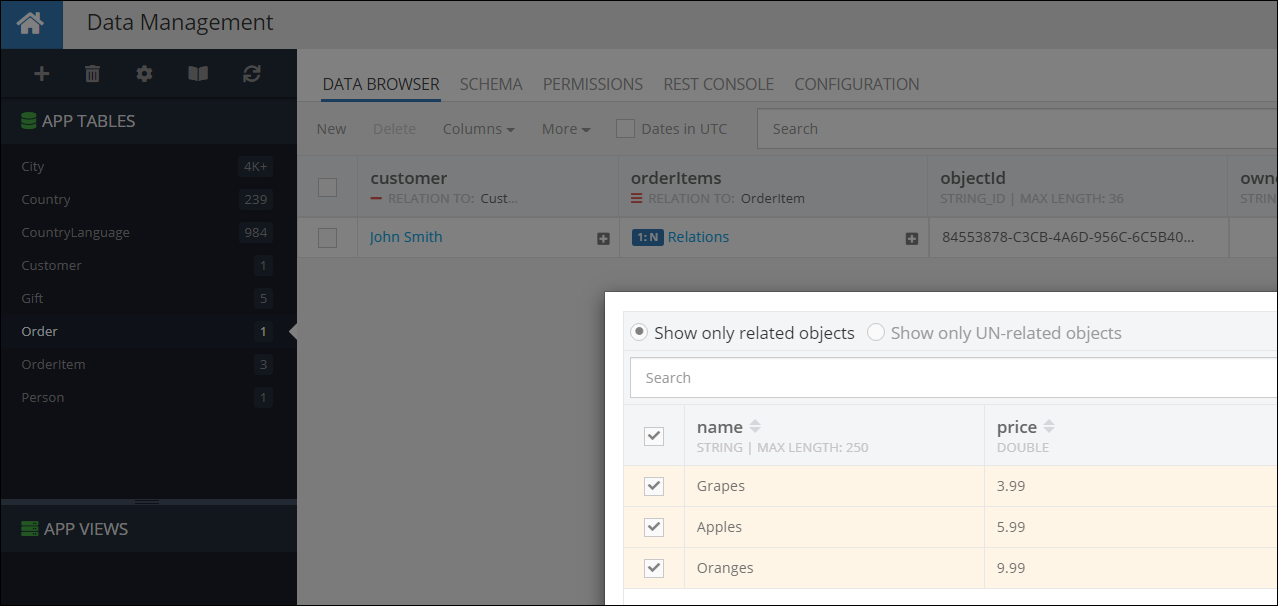
After the code runs, the new OrderItem object is saved in the database and the Order object relation is expanded to include it:
Codeless Reference¶

where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
table name |
Specify the name of the data table where you want to update an existing record. |
object |
An object to update in the database. Object properties must match the names of the table columns. |
return result |
Optional parameter. When this box is checked, the operation returns the updated object. |
The Deep Save API can be used to update an existing object and set a relation with a new child (or parent).
Returns the updated object.
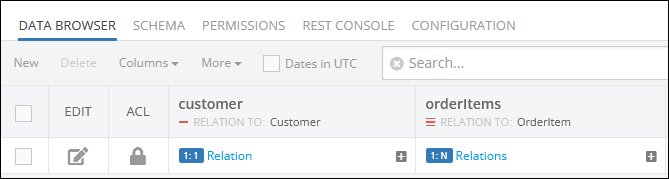
Consider the structure of the data table called Order. This table contains two columns: customer and orderItems. Values in the first column are associated with the Customer data table where the customer names are stored, while values in the second column are related to the OrderItem data table where order details are stored.
Below you can find the structure of the OrderItem data table where order information is stored.
The example below updates the related data table called OrderItem by adding a new object to the Order data table.
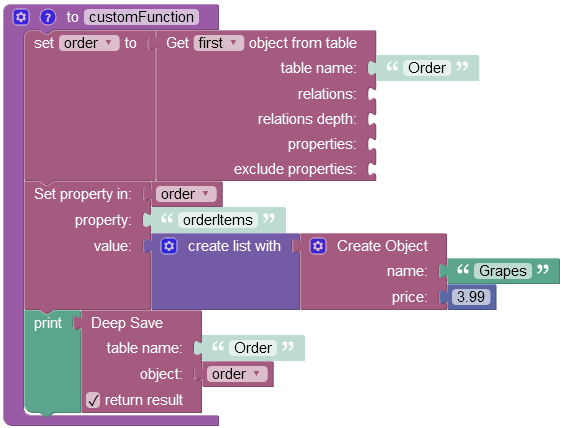
After the Codeless logic runs, the new object gets saved to the OrderItem data table.
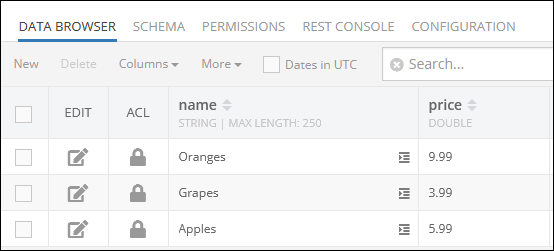
The result of this operation will look as shown below after the Codeless logic runs: