How to Load Data Objects With Related Geopoints Using API
In other articles, we have covered:
- how to declare a geo-to-data relationship in a data table schema and
- how to create relationships between an object in that schema and geopoints.
Of course, both of the operations above can also be accomplished with the API. In this post, we are going to show how to retrieve a data object that has a related geopoint.
Consider the following object:

The Address table has the location column of the GEOPOINT RELATIONSHIP type. There are three data objects in the table and one of them has a related geopoint. The geopoint is shown in the screenshot below.
Notice the geopoint’s metadata (city: NEW YORK CITY ):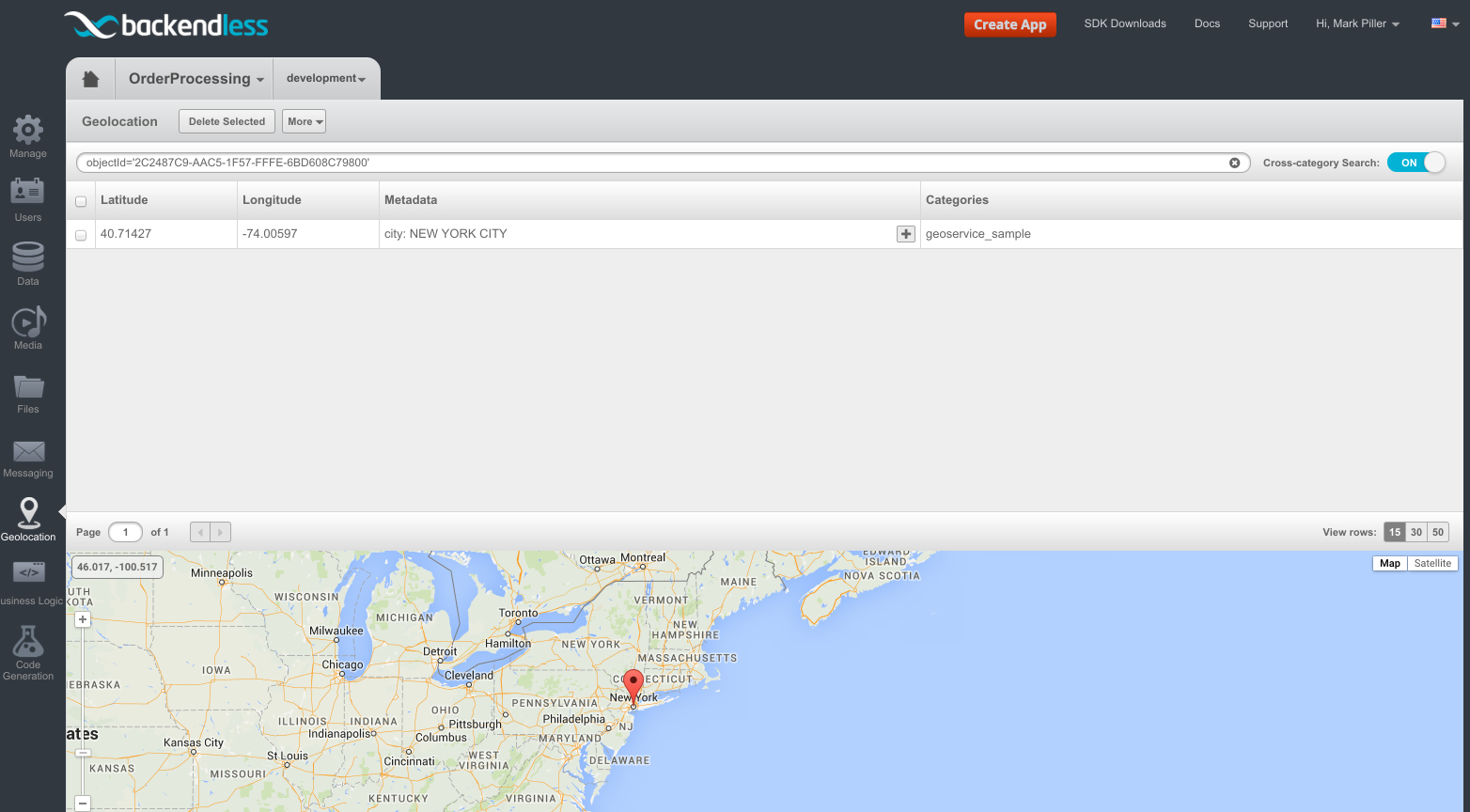
The following code retrieves Address objects using an SQL query. Additionally, the query options include a request for the related “location” property. As a result, when the server returns the Address objects, they will have the location property pre-initialized. This approach is described in greater detail in the “Loading related data objects – the ‘one-step/dynamic’ approach” article:
An object from the Address table should be an instance of the following class.
The package name is irrelevant – it can be anything; however, what’s important is that the location column from the table is represented through the com.backendless.geo.GeoPoint class:
import com.backendless.geo.GeoPoint;
public class Address {
public String street;
public String city;
public GeoPoint location;
}
Code to retrieve data:
DataQueryBuilder dataQuery = DataQueryBuilder.create();
dataQuery.setWhereClause("location.city = 'NEW YORK CITY'");
dataQuery.addRelated("location");
Backendless.Data.of(Address.class).find(dataQuery, new AsyncCallback<List<Address>>() {
@Override
public void handleResponse(List<Address> nycPeople) {
for (Address address : nycPeople) {
Log.i(TAG, "City - " + address.city);
Log.i(TAG, "Location (Geo Point) - " + address.location);
}
}
@Override
public void handleFault(BackendlessFault fault) {
Log.e(TAG, fault.getMessage());
}
});
import com.backendless.geo.GeoPoint data class Address(var street: String? = null, var city: String? = null, var location: GeoPoint? = null)
Code to retrieve data:
val dataQuery = DataQueryBuilder.create()
dataQuery.whereClause = "location.city = 'NEW YORK CITY'"
dataQuery.addRelated("location")
Backendless.Data.of(Address::class.java).find(dataQuery, object : AsyncCallback<List<Address>> {
override fun handleResponse(nycPeople: List<Address>) {
for (address in nycPeople) {
Log.i(TAG, "City - ${address.city}")
Log.i(TAG, "Location (Geo Point) - ${address.location}")
}
}
override fun handleFault(fault: BackendlessFault) {
Log.e(TAG, fault.message)
}
})
@interface Address : NSObject @property (strong, nonatomic) NSString *objectId; @property (strong, nonatomic) NSString *city; @property (strong, nonatomic) NSString *street; @property (strong, nonatomic) GeoPoint *location; @end
Code to retrieve data:
DataQueryBuilder *queryBuilder = [DataQueryBuilder new];
[queryBuilder setWhereClauseWithWhereClause:@"location.city = 'NEW YORK CITY'"];
[queryBuilder setRelatedWithRelated:@[@"location"]];
[[Backendless.shared.data of:[Address class]] findWithQueryBuilder:queryBuilder responseHandler:^(NSArray *addresses) {
for (Address *address in addresses) {
NSLog(@"City - %@", address.city);
NSLog(@"Location (Geo Point) - %@", address.location);
}
} errorHandler:^(Fault *fault) {
NSLog(@"Error: %@", fault.message);
}];
@objcMembers class Address: NSObject {
var objectId: String?
var city: String?
var street: String?
var location: GeoPoint?
}
Code to retrieve data:
let queryBuilder = DataQueryBuilder()
queryBuilder.setWhereClause(whereClause: "location.city = 'NEW YORK CITY'")
queryBuilder.setRelated(related: ["location"])
Backendless.shared.data.of(Address.self).find(queryBuilder: queryBuilder, responseHandler: { addresses in
if let addresses = addresses as? [Address] {
for address in addresses {
print("City - \(address.city ?? "")")
print("Location (Geo Point) - \(address.location ?? GeoPoint())")
}
}
}, errorHandler: { fault in
print("Error: \(fault.message ?? "")")
})
const Backendless = require('backendless')
/*
Or use `import Backendless from 'backendless'` for client side.
If you don't use npm or yarn to install modules, you can add the following line
<script src="//api.backendless.com/sdk/js/latest/backendless.min.js"></script>
to your index.html file and use the global Backendless variable.
*/
Backendless.initApp('YOUR_APP_ID', 'YOUR_JS_API_KEY')
const loadAddresses = () => {
const query = Backendless.DataQueryBuilder.create()
query.setRelated('location')
query.setWhereClause('location.city = \'NEW YORK CITY\'')
return Backendless.Data.of('Address').find(query)
}
const onSuccess = addresses => {
addresses.forEach(address => {
console.log(`City - ${ address.city }`)
console.log(`Location (Geo Point) - ${ JSON.stringify(address.location) }`)
})
}
const onError = error => {
console.error('Server reported an error: ', error.message)
console.error('error code: ', error.code)
console.error('http status: ', error.status)
}
Promise.resolve()
.then(loadAddresses)
.then(onSuccess)
.catch(onError)
DataQueryBuilder dataQuery = DataQueryBuilder();
dataQuery.whereClause = "location.city = 'NEW YORK CITY'";
dataQuery.related = ["location"];
Backendless.Data.of("Address").find(dataQuery).then((nycPeople) {
nycPeople.forEach((address) {
print("City - ${address['city']}");
print("Location (Geo Point) - ${address['location']}");
});
});
The program output is:
City - New York
Location (Geo Point) - GeoPoint{objectId='2C2487C9-AAC5-1F57-FFFE-6BD608C79800', latitude=40.71427, longitude=-74.00597, categories=[geoservice_sample], metadata={city=NEW YORK CITY}, distance=null}