Add Relation using condition¶
This API request adds related objects to the existing collection. Child objects to add to the relation are defined through a whereClause condition.
Method¶
Future<int> Backendless.data.of("TABLE-NAME").addRelation(
String parentObjectId,
String relationColumnName,
{List<String> childrenObjectIds,
String whereClause});
Future<int> Backendless.data.withClass<E>().addRelation(
String parentObjectId,
String relationColumnName,
{List<String> childrenObjectIds,
String whereClause});
where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
TABLE-NAME |
Name of the table where the parent object is stored. |
E |
Dart class of the parent object. The class name identifies the table where the parent object is stored. |
parentObjectId |
The ID of an object which will be assigned related children for relatedColumnName. When this argument is an instance of Map (for the map-based approach), it must contain the "objectId" property. |
relationColumnName |
Name of the column identifying the relation. Objects from the children collection will be added as related for the column in parentObject. The column name may optionally include table name separated by the colon character as well as cardinality which determines the type of relationship (one to one or one to many) (see the note below): |
Important
If the column does not exist in the parent table at the time when the API is called, the value of the "relationColumnName " argument must include the name of the child table separated by colon and the cardinality notation. The cardinality is expressed as ":1 " for one-to-one relations and ":n " for one-to-many relations. For example, the value of "myOrder:Order:1 " will create a one-to-one relation column "myOrder " in the parent table. The column will point to the Order child table. Likewise, the value of "myOrder:Order:n " will create a one-to-many relation column "myOrder " pointing to the Order table.
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
whereClause |
A where clause condition identifying objects in the child table which will be added as related objects to the parent object. |
Return Value¶
Number of child objects added to the relation.
Example¶
The following request adds objects from the Users table to a related property/column the Person object. Child objects added to the relation must match the provided query. The query is specified in the whereClause argument:
name='Joe' or name = 'Frank'.
As a result of the operation, all User objects where the name property is either Joe or Frank will be added to the relation. The relation column is created if it does not exist. This is done because the column contains the child table qualifier, defined as ":Users" right after the column name.
Map parentObject = // parentObject retrieval is out of scope in this example
Backendless.data.of("Person").addRelation(parentObject['objectId'], "users:Users:n",
whereClause: 'name = "Joe" or name = "Frank"').then((response) {
// related object has been added
});
Person personObject = // personObject retrieval is out of scope in this example
Backendless.data.withClass<Person>().addRelation(personObject.objectId, "users:Users:n",
whereClause: 'name = "Joe" or name = "Frank"').then((response) {
// related object has been added
});
Codeless Reference¶
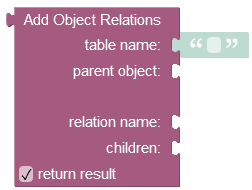
where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
table name |
Name of the table where which contains the parent object as identified by parent object. |
parent object |
Id of the object for which the relation will be created/set. |
relation name |
Name of the column which identifies the relation within the parent table (identified as table-name). The column name may optionally include table name separated by the colon character as well as cardinality which determines the type of relationship (one to one or one to many) (see the note below):If the column does not exist in the parent table at the time when the API is called, the value of the " relationColumnName" argument must include the name of the child table separated by colon and the cardinality notation. The cardinality is expressed as ":1" for one-to-one relations and ":n" for one-to-many relations. For example, the value of "myOrder:Order:1" will create a one-to-one relation column "myOrder" in the parent table. The column will point to the Order child table. Likewise, the value of "myOrder:Order:n" will create a one-to-many relation column "myOrder" pointing to the Order table. |
children |
You must use the where clause condition in this property to select specific children objects from the data table. For more information about where clause conditions, refer to the Search with the Where Clause topic. |
Returns the number of added object relations.
Adding New Relations¶
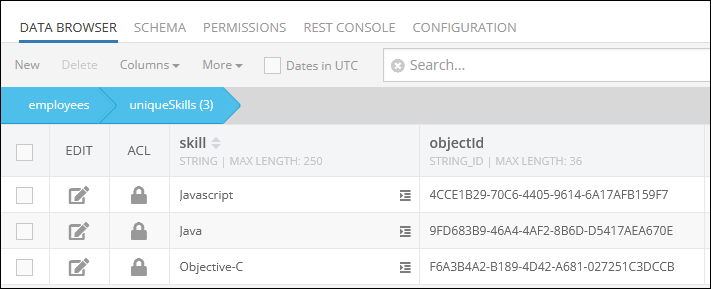
Consider the records stored in the following parent data table called employees. As you can see, this data table contains the skills column that has relation to the child data table called uniqueSkills.
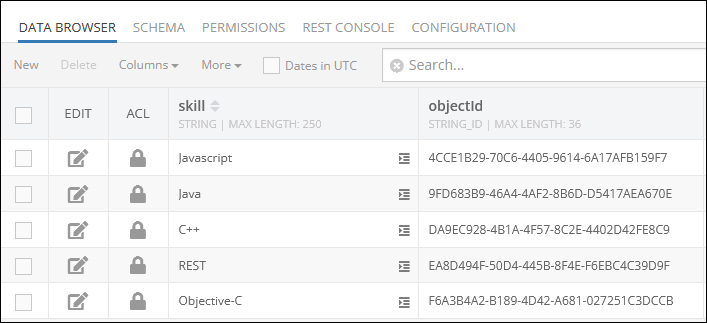
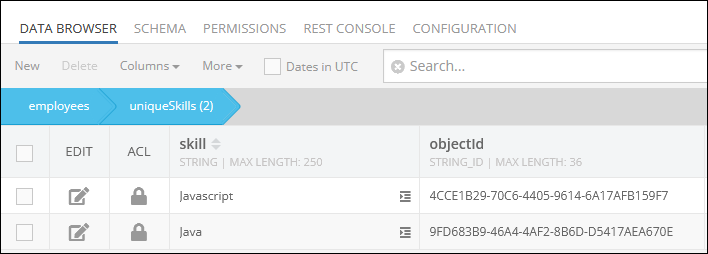
The child data table uniqueSkills contains the following records:
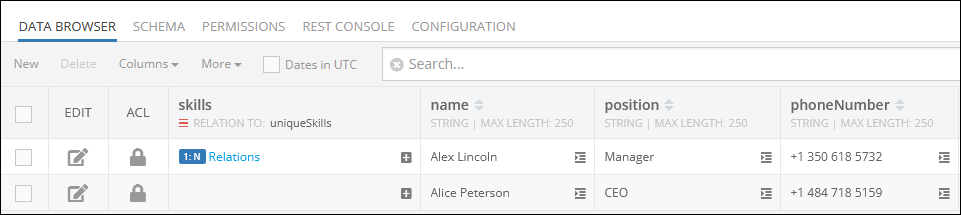
By clicking the value (1:N Relations) in the skills column of the parent data table employees, the system displays currently related objects, which in this case are Java and Javascript.
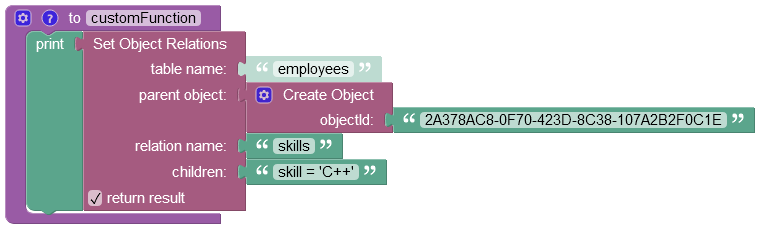
Suppose you need to add a new relation between the parent object (name: Alex``Lincoln, objectId: 2A378AC8-0F70-423D-8C38-107A2B2F0C1E) and the child object with the value "C++" stored in the related data table.
The example below utilizes the where clause expression "skill = 'C++'" specified in the children property which instructs the operation to search the uniqueSkills data table for an object containing the 'C++' value in the "skill" column and establish a new relation with the parent object.
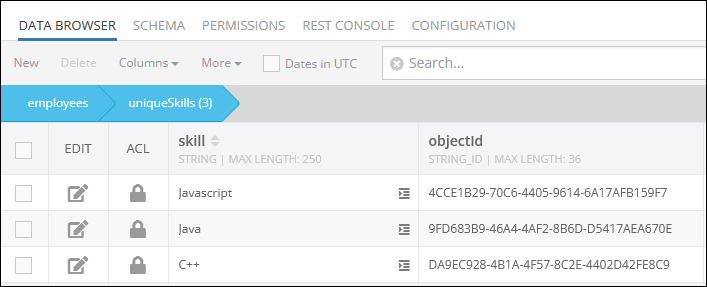
After the Codeless logic, the new relation gets established between the child object and the parent object stored in the employees data table:
Creating Relation Column and Adding New Relations¶
Suppose you have two data tables with no established relations and you need to create a new relation column and add new object relations to the parent object in one request.
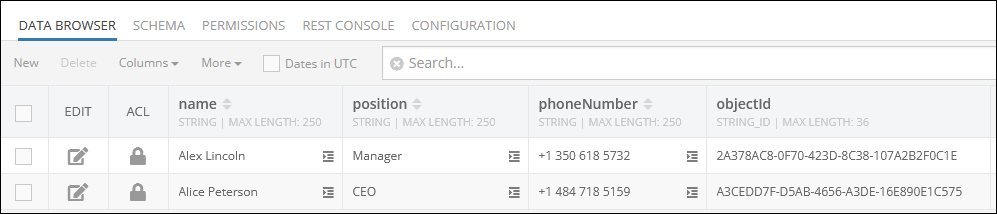
Consider the records in the first data table called employees. As you can see, there is no relation column yet:
Consider the records in the second data table called uniqueSkills:

Imagine you want to establish relations with all objects stored in the uniqueSkills data table except for objects that have values "C++" and "REST" in the skill column.
The example below creates a new column called "skills" in the "employees" data table and establishes one-to-many relations between the parent object (name: Alex Lincoln, objectId: 2A378AC8-0F70-423D-8C38-107A2B2F0C1E) and three children objects from the "uniqueSkills" data table using the where clause condition expressed as "skill != 'C++' and skill != 'REST'" in the children property:
-
(
skill: Javascript, objectId: 4CCE1B29-70C6-4405-9614-6A17AFB159F7) -
(
skill: Java, objectId: 9FD683B9-46A4-4AF2-8B6D-D5417AEA670E) -
(
skill: Objective-C, objectId: F6A3B4A2-B189-4D42-A681-027251C3DCCB)
For the operation to work in this way, you must specify the expression "skills:uniqueSkills:n" in the relation name column. Where "skills" is the name of the relation column to create in the parent data table called "employees", "uniqueSkills" is the name of the child data table where objects are stored, and the ":n" represents the relations cardinality which is one-to-many.
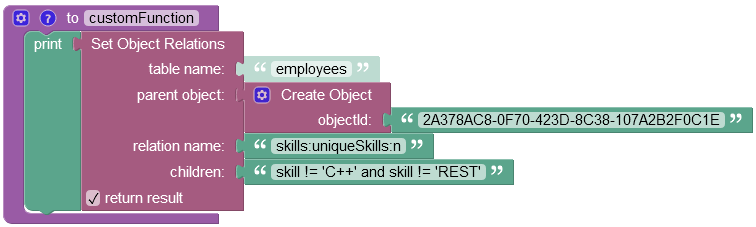
After the Codeless logic runs, the new relation column "skills" gets created in the "employees" data table.
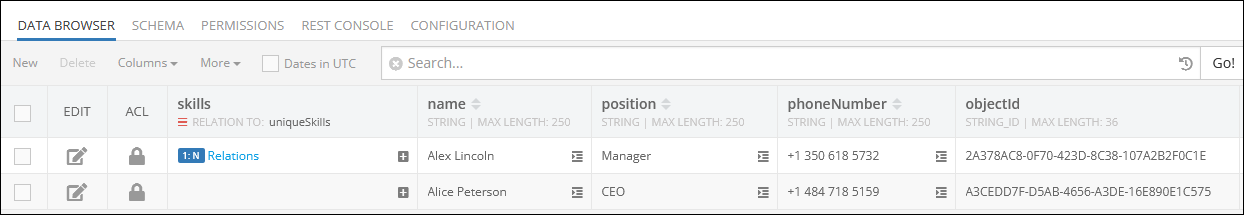
And three new relations are added between the children objects and the parent object stored in the employees data table: