Context Blocks¶
The Context Blocks area in Codeless Logic Designer includes blocks which provide access to the "contextual" information. For the API services these include:
Method arguments blocks (if any are declared)¶
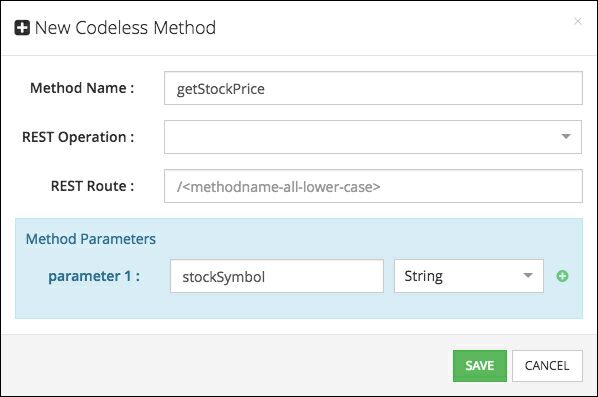
If a service method is created with parameters, they can be accessed using special blocks. Consider the following service method declaration which includes a parameter:
When editing the method's logic in the Logic Designer, it shows the block for the argument in the Context Blocks section:
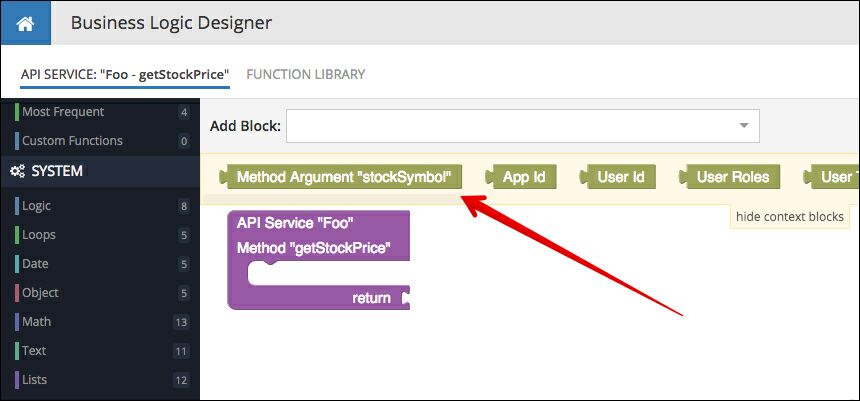
When using the "method argument" block, it returns the value sent by the client in the method invocation.
Request Info Blocks¶
- Application ID - id of the application in which context the method is invoked.
-
User ID -
objectIdof the currently logged in user whose identity is used to invoke the method. A value for this parameter is not present if there is no logged in user (or if theuser-tokenheader is not passed for the REST invocations).
-
User Roles - an array/list of the role names of the logged-in user (if any) who made the API service call.

-
User Token - value of the user-token header sent by the client application when invoking the service
-
Device Type - the type of the device (as a string value) which initiated the method invocation. Possible values are
"IOS","ANDROID","JS","REST","BL"(business logic)
-
Request Path - path in the request URL which identifies the invoked method. This is the part of the URL which comes after
<service version>: in the complete service request URL:https://api.backendless.com/<App ID>/<REST API key>/services/<service name>/<service version>/<method's REST route>?params
-
Request Headers - HTTP headers sent by the client application when invoking the service.

-
Request Path Parameters - if the service operation is declared with a parameterized custom REST route, the parameters can be accessed with the following block:

-
Request Query Parameters - all parameters for the methods recognized or declared as HTTP GET must be sent in the URL's query string. Service logic can use the following block to get access to these parameters: