Overview¶
An event handler is a custom, server-side code which responds to an API event. For every API call Backendless generates two types of events - "before" and "after". The before event is fired before the default logic of the API implementation is executed and the "after" event is triggered right after the default API implementation logic. An event handler can respond to either one of these events. A synchronous (blocking) event handler participates in the API invocation chain and can modify the objects in the chain's flow. For example, the "before" event handlers can modify arguments of the API calls, so the default logic gets the modified objects. Similarly, an "after" handler can modify the return value (or exception) so the client application which made the API request receives the modified value. The diagram below illustrates the flow:
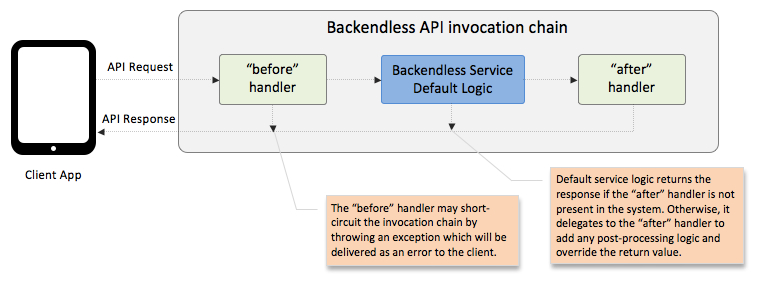
All built-in Backendless services emit the "before" and "after" events for every API call. The only exception to this rule is when an API is invoked from server code (for example in a beforeFind handler your code makes an Update API call). This limitation is in place to prevent infinite recursive invocations which may drain the computing resources.
Consider the following example which is an API event handler for the "beforeCreate" API event. The event is triggered when a client application saves an object into the "Contact" data table:
package com.consoledemo.events.persistence_service;
import com.backendless.servercode.RunnerContext;
import com.backendless.servercode.annotation.Asset;
import com.backendless.servercode.extension.PersistenceExtender;
import com.consoledemo.models.Contact;
@Asset( "Contact" )
public class ContactTableEventHandler extends PersistenceExtender<Contact>
{
@Override
public void beforeCreate( RunnerContext context, Contact contact) throws Exception
{
// add your code here
}
}
@Asset annotation specifies the "asset" or in this case a data table for which the event will be triggered.
* The class extends com.backendless.servercode.extension.PersistenceExcender. This is required in order for the custom code to inject itself into the API invocation handling chain. Every API service has its own extender class which must be derived from by the an API event handler.
* The beforeCreate method is the event handler method. The name of the method indicates it will be invoked before the default implementation logic of the create method from the Data service API.
* The event handler method has the same signature as the corresponding method from the Data service with the exception of the RunnerContext argument.