Get Object Count¶
The Object Count API provides a way to obtain the following values from the server:
- Number of objects in a table
- Number of objects matching query
- Number of related objects
Method¶
Future<int> Backendless.data.of("TABLE-NAME").getObjectCount([DataQueryBuilder queryBuilder]);
Future<int> Backendless.data.withClass<E>().getObjectCount([DataQueryBuilder queryBuilder]);
where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
TABLE-NAME |
Name of the table where to calculate the object count. |
E |
Java class of the data object which identifies the table where to calculate the object count. |
queryBuilder |
Instance of com.backendless.persistence.DataQueryBuilder. When present in the arguments, the object must contain a whereClause query. The query is used by the server to identify a collection of objects. |
Return Value¶
The integer value which is the object count.
Example¶
Total object count for a table¶
The following sample request retrieves total number of objects in table Order:
Backendless.data.of("Order").getObjectCount().then((count) {
print("Total objects in the Order table - $count");
});
import 'package:backendless_sdk/backendless_sdk.dart';
@reflector
class Order {
String objectId;
int orderAmount;
}
Backendless.data.withClass<Order>().getObjectCount().then((count) {
print("Total objects in the Order table - $count");
});
Object count for a query¶
The following sample request retrieves total number of objects in table Order which satisfy the condition of orderAmount > 100:
DataQueryBuilder queryBuilder = DataQueryBuilder()
..whereClause = "orderAmount > 100";
Backendless.data.of("Order").getObjectCount(queryBuilder).then((count) {
print("Found objects - $count");
});
DataQueryBuilder queryBuilder = DataQueryBuilder()
..whereClause = "orderAmount > 100";
Backendless.data.withClass<Order>().getObjectCount(queryBuilder).then((count) {
print("Total objects in the Order table - $count");
});
Related object count¶
The following sample request retrieves total number of related "child" objects for a parent object. The parent table is Person. It contains a relation column called address pointing to the Addresstable. The query below retrieves a count of related child objects for a parent object with objectID of XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX. The whereClause query syntax for this scenario is:Person[address].objectId = 'XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX'
DataQueryBuilder queryBuilder = DataQueryBuilder()
..whereClause = "Person[address].objectId = 'XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX'";
Backendless.data.of("Address").getObjectCount(queryBuilder).then((count) {
print("Found objects - $count");
});
DataQueryBuilder queryBuilder = DataQueryBuilder()
..whereClause = "Person[address].objectId = 'XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX'";
Backendless.data.withClass<Address>().getObjectCount(queryBuilder).then((count) {
print("Found objects - $count");
});
Codeless Reference¶
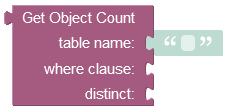
where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
table name |
Name of the data table where to calculate the object count. |
where clause |
Optional argument. If set, it is a search query used by the server it to determine the number of objects matching the condition. Refer to the Search With The Where Clause topic for more information. |
distinct |
Used to return unique objects from the data table. Only custom properties/columns are considered in the query. Hence, if the data table contains a duplicate object, then it is not counted in the operation. |
Returns the number of objects in a table (if the where clause is not set), otherwise the number of objects matching the search query.
Consider the following records in the employees data table:
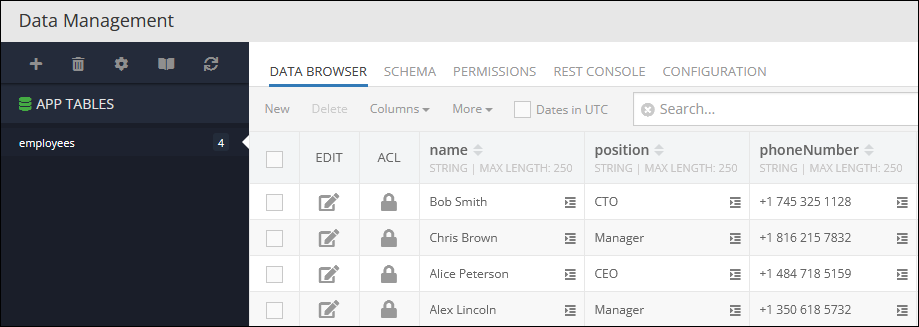
The example below counts specific objects in the data table since the where clause condition is set to exclude objects that contain the value 'Manager' in the column position. Thereby, objects with the 'Manager' values in the position column are not counted in the operation.
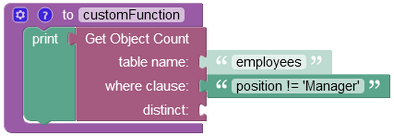
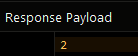
The result of this operation will look as shown below after the Codeless logic runs:
Consider the data table below that contains two duplicate objects:
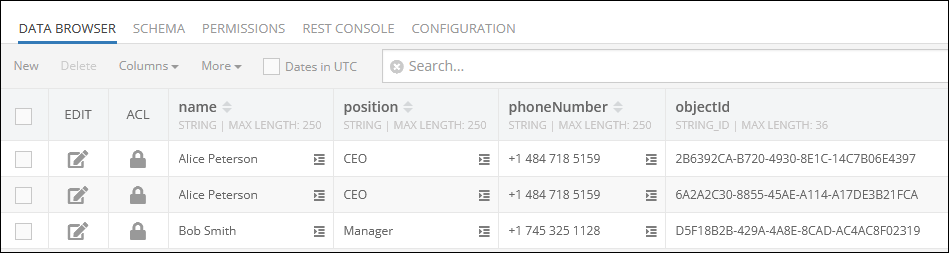
The Codeless logic below has a where clause condition which is set to include in the operation only those objects that contain the value 'CEO' in the position column. The distinct parameter is set to true, hence the operation is set to count only unique objects, duplicates are skipped.
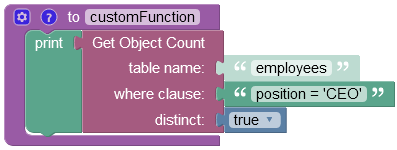
The result of this operation will look as shown below after the Codeless logic runs: