Delete Objects from relation¶
The API removes specific objects from a relationship with their parent.
Method¶
Future<int> Backendless.data.of("TABLE-NAME").deleteRelation(
String parentObjectId,
String relationColumnName,
{List<String> childrenObjectIds,
String whereClause});
Future<int> Backendless.data.withClass<E>(). deleteRelation(
String parentObjectId,
String relationColumnName,
{List<String> childrenObjectIds,
String whereClause});
where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
TABLE-NAME |
Name of the table where the parent object is stored. |
E |
Dart class of the parent object. The class name identifies the table where the parent object is stored. |
parentObjectId |
The ID of an object for which the relation with the specified children will be deleted. When this argument is an instance of Map (for the map-based approach), it must contain the "objectId" property. |
relationColumnName |
Name of the column identifying the relation. Relationship between the specified objects from the children collection will be deleted for the column in parentObject. |
childrenObjectIds |
A collection of child object IDs for which the relationship with the parentObject will be deleted. |
Return Value¶
Number of child objects for which the relationship has been deleted.
Example¶
The example below deletes a relation between a Person object and its children. The child objects are referenced explicitly in the API call (see the object IDs in the collection as "XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX" ``and`` "ZZZZ-ZZZZ-ZZZZZ-ZZZZZ").The relation column is address.
Map parentObject = // parentObject retrieval is out of scope in this example
Map childObject1 = // childObject retrieval is out of scope in this example
Map childObject2 = // childObject retrieval is out of scope in this example
Backendless.data.of("Person"). deleteRelation(parentObject['objectId'], "address",
children: [childObject1['objectId'], childObject2['objectId']]).then((response) {
// relation has been deleted
});
Person personObject = // personObject retrieval is out of scope in this example
Address addressObject1 = // addressObject retrieval is out of scope in this example
Address addressObject2 = // addressObject retrieval is out of scope in this example
Backendless.data.withClass<Person>(). deleteRelation(personObject.objectId, "address",
children: [addressObject1.objectId, addressObject2.objectId]).then((response) {
// relation has been deleted
});
Codeless Reference¶
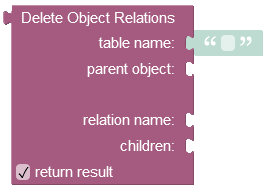
where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
table name |
Name of the table where which contains the parent object as identified by parent object. |
parent object |
Id of the object for which the relation will be deleted. |
relation name |
Name of the column which identifies the relation within the parent table (identified as table name). |
children |
Represents a list containing unique identifiers(objectIds) of the children objects relations that must be deleted from the data table. |
return result |
When this box is checked, the operation returns the number of removed child objects relations. |
Returns the number of removed child objects relations.
Consider the first object with one-to-many relations(skills column) in the parent data table called employees: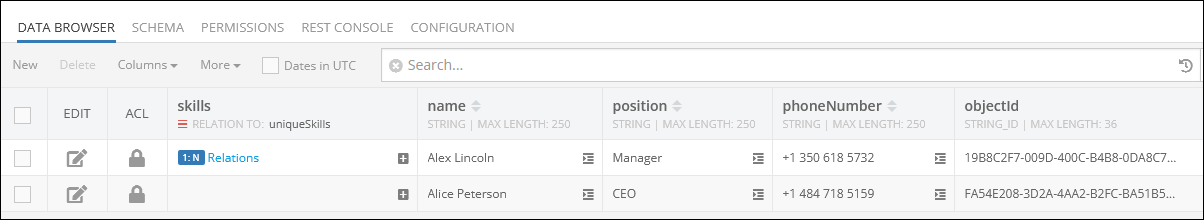
By clicking the record (1:N Relations) in the skills column of the parent data table presented above, you get redirected to the child data table called uniqueSkills, where you can see the related children objects:
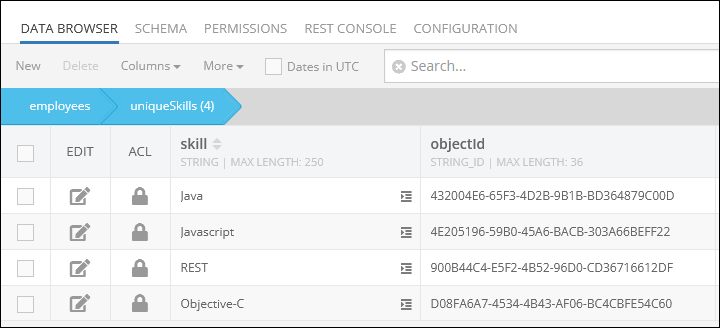
Suppose you want to remove two relations. The following example demonstrates the removal of the Objective-C and Javascript relations from the parent object:
The objectId values for each relation are:
-
Objective-C:"4E205196-59B0-45A6-BACB-303A66BEFF22" -
Javascript:"D08FA6A7-4534-4B43-AF06-BC4CBFE54C60"
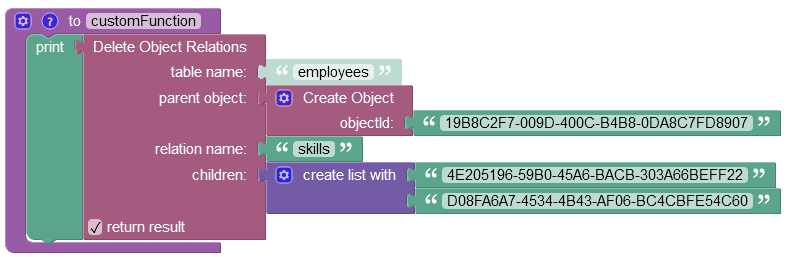
After the operation runs, the Objective-C and Javascript relations get deleted.