Delete Relation using condition¶
API request must identify the child objects to delete from the relation implicitely through a whereClause condition.
Method¶
Future<int> Backendless.data.of("TABLE-NAME"). deleteRelation(
String parentObjectId,
String relationColumnName,
{List<String> childrenObjectIds,
String whereClause});
Future<int> Backendless.data.withClass<E>(). deleteRelation(
String parentObjectId,
String relationColumnName,
{List<String> childrenObjectIds,
String whereClause});
where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
TABLE-NAME |
Name of the table where the parent object is stored. |
E |
Dart class of the parent object. The class name identifies the table where the parent object is stored. |
parentObjectId |
The ID of an object for which the relation with the identified children will be deleted. When this argument is an instance of Map (for the map-based approach), it must contain the "objectId" property. |
relationColumnName |
Name of the column representing the relation. Relationship between the child objects identified by whereClause will be deleted for this column in parentObject. |
whereClause |
A where clause condition identifying the objects in the child table which will be removed from the relation to the parent object. |
Return Value¶
Number of child objects removed from the relationship.
Example¶
The following request deletes a relation between a Person object and all the related objects in the related table identified by column "user" which match the provided query:
name='Joe' or name = 'Frank'
As a result of the operation, all related objects where the name property is either Joe or Frank will be deleted from the relation.
Map parentObject = // parentObject retrieval is out of scope in this example
Backendless.data.of("Person"). deleteRelation(parentObject['objectId'], "user",
whereClause: 'name = "Joe" or name = "Frank"').then((response) {
// relation has been deleted
});
Person personObject = // personObject retrieval is out of scope in this example
Backendless.data.withClass<Person>(). deleteRelation(personObject.objectId, "user",
whereClause: 'name = "Joe" or name = "Frank"').then((response) {
// relation has been deleted
});
Codeless Reference¶
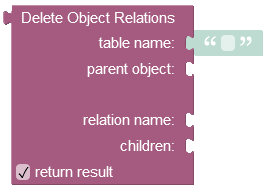
where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
table name |
Name of the table where which contains the parent object as identified by parent object. |
parent object |
Id of the object for which the relation will be deleted. |
relation name |
Name of the column which identifies the relation within the parent table (identified as table name). |
children |
You must use the where clause condition in this property to delete specific children objects from the data table. |
return result |
When this box is checked, the operation returns the number of removed child objects relations. |
Returns the number of removed child objects relations.
Consider the first object with one-to-many relations(skills column) in the parent data table called employees: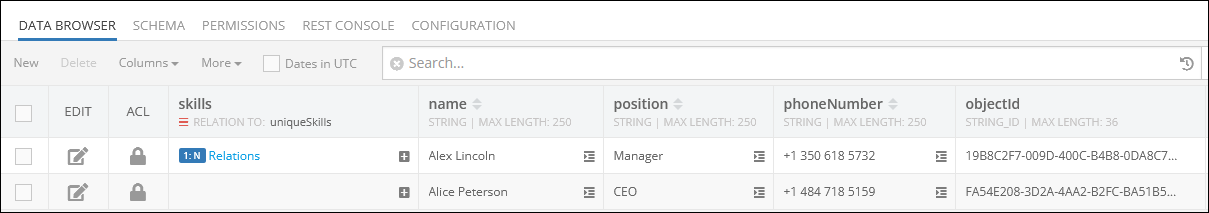
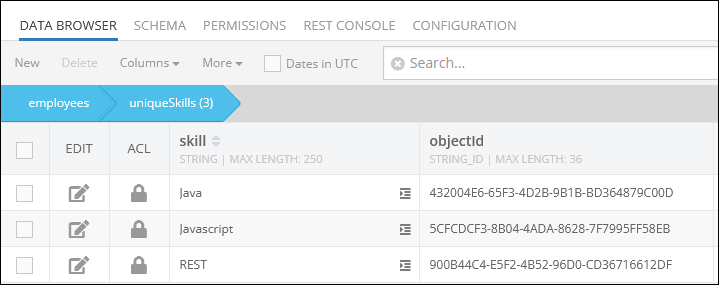
By clicking the record (1:N Relations) in the skills column of the parent data table presented above, you get redirected to the child data table called uniqueSkills, where you can see the related children objects:
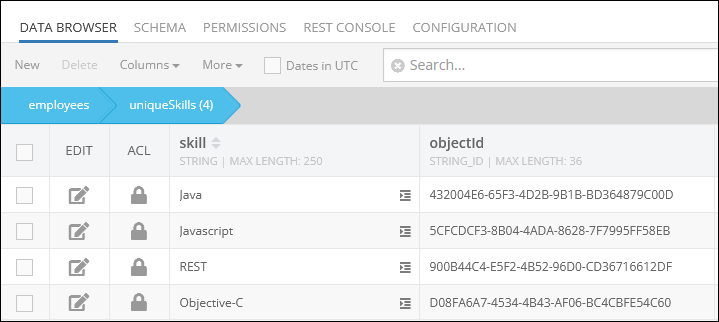
Suppose, you want to delete only one relation. The example below deletes the Objective-C relation from the data table using the where clause condition "skill = 'Objective-C'" specified in the children property:
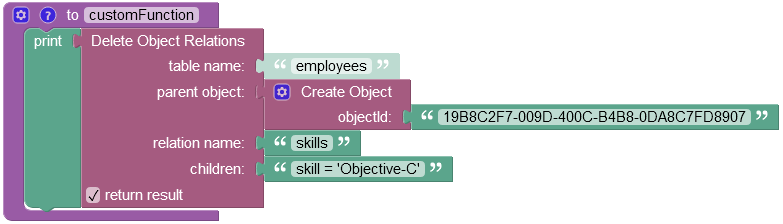
The result of this operation is one deleted relation Objective-C from the data table:
In case you want to delete multiple objects relations using the where clause condition, refer to the example below which removes all relations except the Java.
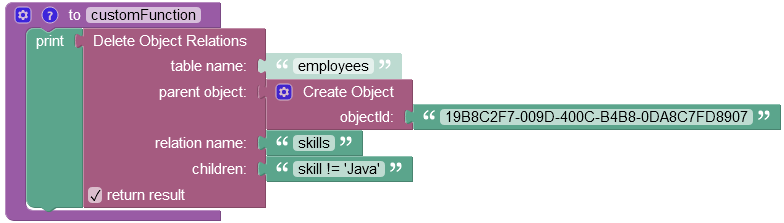
After the Codeless Logic runs, only one object relation Java remains in the data table.