Welcome¶
Welcome to Backendless, a powerful application backend and API services platform. The platform is designed to provide highly scalable backend functionality for mobile and web applications. Backendless consists of built-in, general purpose backend functionality and also supports deployment of custom, developer-defined API services and functions which can be executed as serverless blocks of logic. The built-in functions support common backend tasks and operations such as user login and logout, password recovery, data persistence, file upload, etc. Developer-defined API services and functions can be used for custom server-side business logic. The diagram below illustrates major components of the Backendless architecture:
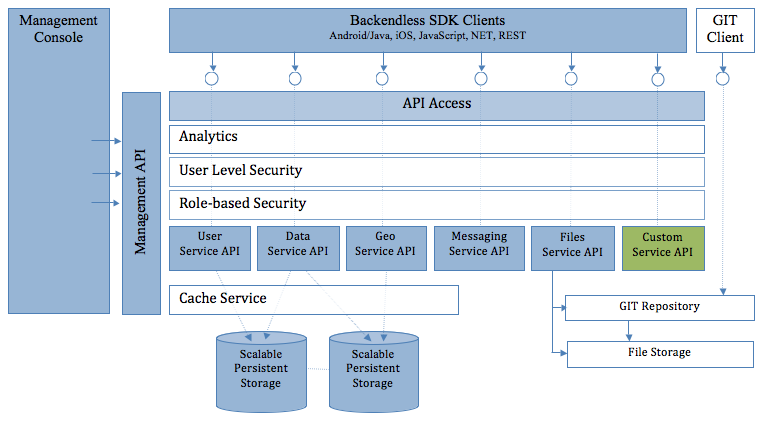
The sections below describe individual service APIs. It is recommended to go through the Setup section first to configure your environment.