Basic Object Retrieval¶
Backendless supports multiple data search and retrieval operations. These include finding an object by its objectId, finding first or last object in the collection or retrieving the entire persisted collection.
Retrieving Data Objects¶
Retrieving object count for a table/query can be done with a 'data store' object. A reference to a data store can be obtained using the following code:
// obtaining DataStore for the NSDictionary approach
MapDrivenDataStore *dataStore = [Backendless.shared.data ofTable:@"TABLE-NAME"];
// obtaining DataStore for the custom-class approach
DataStoreFactory *dataStore = [Backendless.shared.data of:[YOUR-CLASS class]];
// obtaining DataStore for the NSDictionary approach
let dataStore = Backendless.shared.data.ofTable("YOUR-TABLE")
// obtaining DataStore for the custom-class approach
let dataStore = Backendless.shared.data.of(YOUR-CLASS.self)
where
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
YOUR-CLASS |
identifies a table on the server. |
"TABLE-NAME" |
the name of the table for which to get the data store. All subsequent data store operations will be performed in the specified table. |
A data store object provides the following APIs for basic data retrieval from Backendless:
Basic retrieval of data objects¶
Paging is built-in and the server returns up to 100 objects at a time.
- (void)findWithResponseHandler:^(NSArray * _Nonnull)responseHandler errorHandler:^(Fault * _Nonnull)errorHandler;
func find(responseHandler: (([Any]) -> Void)!, errorHandler: ((Fault) -> Void)!)
Find first data object¶
The first data object is the first one saved in the data store:
- (void)findFirstWithResponseHandler:^(id _Nonnull)responseHandler errorHandler:^(Fault * _Nonnull)errorHandler;
func findFirst(responseHandler: ((Any) -> Void)!, errorHandler: ((Fault) -> Void)!)
Find first data object with queryBuilder¶
The first data object is the first one saved in the data store:
- (void))findFirstWithQueryBuilder:(DataQueryBuilder *)queryBuilder responseHandler:^(NSDictionary<NSString *,id> *)responseHandler errorHandler:^(Fault *)errorHandler;
public func findFirst(queryBuilder: DataQueryBuilder, responseHandler: (([String : Any]) -> Void)!, errorHandler: ((Fault) -> Void)!)
Find last data object¶
The last data object is the last one saved in the data store:
- (void)findLastWithResponseHandler:^(id _Nonnull)responseHandler errorHandler:^(Fault * _Nonnull)errorHandler;
func findLast(responseHandler: ((Any) -> Void)!, errorHandler: ((Fault) -> Void)!)
Find last data object with queryBuilder¶
The last data object is the last one saved in the data store:
- (void))findLastWithQueryBuilder:(DataQueryBuilder *)queryBuilder responseHandler:^(NSDictionary<NSString *,id> *)responseHandler errorHandler:^(Fault *)errorHandler;
public func findLast(queryBuilder: DataQueryBuilder, responseHandler: (([String : Any]) -> Void)!, errorHandler: ((Fault) -> Void)!)
Find a data object by object ID¶
- (void)findByIdWithObjectId:(NSString * _Nonnull)objectId responseHandler:^(id _Nonnull)responseHandler errorHandler:^(Fault * _Nonnull)errorHandler;
func findById(objectId: String, responseHandler: ((Any) -> Void)!, errorHandler: ((Fault) -> Void)!)
Basic retrieval of data objects¶
Paging is built-in and the server returns up to 100 objects at a time.
- (void)findWithResponseHandler:^(NSArray<NSDictionary<NSString *,id> *> * _Nonnull)responseHandler errorHandler:^(Fault * _Nonnull)errorHandler;
func find(responseHandler: (([[String : Any]]) -> Void)!, errorHandler: ((Fault) -> Void)!)
Find first data object¶
The first data object is the first one saved in the data store:
- (void)findFirstWithResponseHandler:^(NSDictionary<NSString *,id> * _Nonnull)responseHandler errorHandler:^(Fault * _Nonnull)errorHandler;
func findFirst(responseHandler: (([String : Any]) -> Void)!, errorHandler: ((Fault) -> Void)!)
Find last data object¶
The last data object is the last one saved in the data store:
- (void)findLastWithResponseHandler:^(NSDictionary<NSString *,id> * _Nonnull)responseHandler errorHandler:^(Fault * _Nonnull)errorHandler;
func findLast(responseHandler: (([String : Any]) -> Void)!, errorHandler: ((Fault) -> Void)!)
Find a data object by object ID¶
- (void)findByIdWithObjectId:(NSString * _Nonnull)objectId responseHandler:^(NSDictionary<NSString *,id> * _Nonnull)responseHandler errorHandler:^(Fault * _Nonnull)errorHandler;
func findById(objectId: String, responseHandler: (([String : Any]) -> Void)!, errorHandler: ((Fault) -> Void)!)
where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
objectId |
object ID of the object to find. For the details about objectId, see the Data Object section of the documentation. |
responseHandler |
handles successful result of an asynchronous call. |
errorHandler |
handles fault result of an asynchronous call. |
queryBuilder |
Instance of com.backendless.persistence.DataQueryBuilder. When present in the arguments, the object must contain a whereClause query. The query is used by the server to identify a collection of objects. |
Signatures: Find a data object by object ID with the queryBuilder parameter.¶
- (void)findByIdWithObjectId:(NSString * _Nonnull)objectId queryBuilder:(DataQueryBuilder * _Nonnull)queryBuilder responseHandler:^(id _Nonnull)responseHandler errorHandler:^(Fault * _Nonnull)errorHandler;
func findById(objectId: String, queryBuilder: DataQueryBuilder, responseHandler: ((Any) -> Void)!, errorHandler: ((Fault) -> Void)!)
- (void)findByIdWithObjectId:(NSString * _Nonnull)objectId queryBuilder:(DataQueryBuilder * _Nonnull)queryBuilder responseHandler:^(NSDictionary<NSString *,id> * _Nonnull)responseHandler errorHandler:^(Fault * _Nonnull)errorHandler;
func findById(objectId: String, queryBuilder: DataQueryBuilder, responseHandler: (([String : Any]) -> Void)!, errorHandler: ((Fault) -> Void)!)
Example: Find a data object by object ID with the queryBuilder parameter.¶
- (void)findByIdWithObjectId:(NSString * _Nonnull)objectId queryBuilder:(DataQueryBuilder * _Nonnull)queryBuilder responseHandler:^(id _Nonnull)responseHandler errorHandler:^(Fault * _Nonnull)errorHandler;
func findById(objectId: String, queryBuilder: DataQueryBuilder, responseHandler: ((Any) -> Void)!, errorHandler: ((Fault) -> Void)!)
- (void)findByIdWithObjectId:(NSString * _Nonnull)objectId queryBuilder:(DataQueryBuilder * _Nonnull)queryBuilder responseHandler:^(NSDictionary<NSString *,id> * _Nonnull)responseHandler errorHandler:^(Fault * _Nonnull)errorHandler;
func findById(objectId: String, queryBuilder: DataQueryBuilder, responseHandler: (([String : Any]) -> Void)!, errorHandler: ((Fault) -> Void)!)
- (void)findByIdWithObjectId:(NSString * _Nonnull)objectId queryBuilder:(DataQueryBuilder * _Nonnull)queryBuilder responseHandler:^(NSDictionary<NSString *,id> * _Nonnull)responseHandler errorHandler:^(Fault * _Nonnull)errorHandler;
func findById(objectId: String, queryBuilder: DataQueryBuilder, responseHandler: (([String : Any]) -> Void)!, errorHandler: ((Fault) -> Void)!)
where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
queryBuilder |
Instance of com.backendless.persistence.DataQueryBuilder. When present in the arguments, the object must contain a whereClause query. The query is used by the server to identify a collection of objects. |
objectId |
object ID of the object to find. For the details about objectId, see the Data Object section of the documentation. |
responseHandler |
handles successful result of an asynchronous call. |
errorHandler |
handles fault result of an asynchronous call. |
Return Value¶
Most methods return a single object (findFirst, findList, findById), the find method returns an array of objects. The array contains objects of the specified class with the "Custom class approach" or dictionaries/maps with the "Dictionary approach".
Example¶
// Consider the following class:
@interface Contact : NSObject
@property (strong, nonatomic) NSString *objectId;
@property (strong, nonatomic) NSString *name;
@property (strong, nonatomic) NSString *phone;
@property (strong, nonatomic) NSString *title;
@property (strong, nonatomic) NSNumber *age;
@end
// The following code demonstrates various search queries:
//
// Example: Load objects from the "Contact" table:
DataStoreFactory *dataStore = [Backendless.shared.data of:[Contact class]];
[dataStore findWithResponseHandler:^(NSArray *foundObjects) {
NSLog(@"Found objects: %@", foundObjects);
} errorHandler:^(Fault *fault) {
NSLog(@"Error: %@", fault.message);
}];
// Example: Find the first object in the "Contact" table:
DataStoreFactory *dataStore = [Backendless.shared.data of:[Contact class]];
[dataStore findFirstWithResponseHandler:^(Contact *first) {
NSLog(@"Found first: %@", first);
} errorHandler:^(Fault *fault) {
NSLog(@"Error: %@", fault.message);
}];
// Example: Find the last object in the "Contact" table:
DataStoreFactory *dataStore = [Backendless.shared.data of:[Contact class]];
[dataStore findLastWithResponseHandler:^(Contact *last) {
NSLog(@"Found last: %@", last);
} errorHandler:^(Fault *fault) {
NSLog(@"Error: %@", fault.message);
}];
// Example: Find object by object ID:
DataStoreFactory *dataStore = [Backendless.shared.data of:[Contact class]];
[dataStore findByIdWithObjectId:@"862D8AB3-02F1-4932-FF70-527C3638B200" responseHandler:^(Contact *foundObject) {
NSLog(@"Found by id: %@", foundObject);
} errorHandler:^(Fault *fault) {
NSLog(@"Error: %@", fault.message);
}];
// Consider the following class:
// Swift note: The @objcMembers attribute is important.
// It is required since the Swift object properties are accessed
// from the Objective-C runtime.
@objcMembers class Contact: NSObject {
var objectId: String?
var name: String?
var phone: String?
var title: String?
var age: NSNumber?
}
// The following code demonstrates various search queries:
// Example: Load objects from the "Contact" table:
let dataStore = Backendless.shared.data.of(Contact.self)
dataStore.find(responseHandler: { foundObjects in
print("Found objects: \(foundObjects as! [Contact])")
}, errorHandler: { fault in
print("Error: \(fault.message ?? "")")
})
// Example: Find the first object in the "Contact" table:
let dataStore = Backendless.shared.data.of(Contact.self)
dataStore.findFirst(responseHandler: { first in
print("Found first: \(first as! Contact)")
}, errorHandler: { fault in
print("Error: \(fault.message ?? "")")
})
// Example: Find the last object in the "Contact" table:
let dataStore = Backendless.shared.data.of(Contact.self)
dataStore.findLast(responseHandler: { last in
print("Found last: \(last as! Contact)")
}, errorHandler: { fault in
print("Error: \(fault.message ?? "")")
})
// Example: Find object by object ID:
let dataStore = Backendless.shared.data.of(Contact.self)
dataStore.findById(objectId: "862D8AB3-02F1-4932-FF70-527C3638B200", responseHandler: { foundObject in
print("Found object: \(foundObject as! Contact)")
}, errorHandler: { fault in
print("Error: \(fault.message ?? "")")
})
// Dictionary-driven approach does not require
// a class definition for objects stored in Backendless.
// The following code demonstrates various search queries:
// Example: Load objects from the "Contact" table:
MapDrivenDataStore *dataStore = [Backendless.shared.data ofTable:@"Contact"];
[dataStore findWithResponseHandler:^(NSArray *foundObjects) {
NSLog(@"Found objects: %@", foundObjects);
} errorHandler:^(Fault *fault) {
NSLog(@"Error: %@", fault.message);
}];
// Example: Find the first object in the "Contact" table:
MapDrivenDataStore *dataStore = [Backendless.shared.data ofTable:@"Contact"];
[dataStore findFirstWithResponseHandler:^(NSDictionary *first) {
NSLog(@"Found first: %@", first);
} errorHandler:^(Fault *fault) {
NSLog(@"Error: %@", fault.message);
}];
// Example: Find the last object in the "Contact" table:
MapDrivenDataStore *dataStore = [Backendless.shared.data ofTable:@"Contact"];
[dataStore findLastWithResponseHandler:^(NSDictionary *last) {
NSLog(@"Found last: %@", last);
} errorHandler:^(Fault *fault) {
NSLog(@"Error: %@", fault.message);
}];
// Example: Find object by object ID:
MapDrivenDataStore *dataStore = [Backendless.shared.data ofTable:@"Contact"];
[dataStore findByIdWithObjectId:@"862D8AB3-02F1-4932-FF70-527C3638B200" responseHandler:^(NSDictionary *foundObject) {
NSLog(@"Found by id: %@", foundObject);
} errorHandler:^(Fault *fault) {
NSLog(@"Error: %@", fault.message);
}];
// Dictionary-driven approach does not require
// a class definition for objects stored in Backendless.
// The following code demonstrates various search queries:
// Example: Load objects from the "Contact" table:
let dataStore = Backendless.shared.data.ofTable("Contact")
dataStore.find(responseHandler: { foundObjects in
print("Found objects: \(foundObjects as! [[String: Any]])")
}, errorHandler: { fault in
print("Error: \(fault.message ?? "")")
})
// Example: Find the first object in the "Contact" table:
let dataStore = Backendless.shared.data.ofTable("Contact")
dataStore.findFirst(responseHandler: { first in
print("Found first: \(first as! [String: Any])")
}, errorHandler: { fault in
print("Error: \(fault.message ?? "")")
})
// Example: Find the last object in the "Contact" table:
let dataStore = Backendless.shared.data.ofTable("Contact")
dataStore.findLast(responseHandler: { last in
print("Found last: \(last as! [String: Any])")
}, errorHandler: { fault in
print("Error: \(fault.message ?? "")")
})
// Example: Find object by object ID:
let dataStore = Backendless.shared.data.ofTable("Contact")
dataStore.findById(objectId: "862D8AB3-02F1-4932-FF70-527C3638B200", responseHandler: { foundObject in
print("Found object: \(foundObject as! [String: Any])")
}, errorHandler: { fault in
print("Error: \(fault.message ?? "")")
})
Example Find the first object in the "Person" table with the queryBuilder parameter.
DataQueryBuilder *queryBuilder = [DataQueryBuilder new];
queryBuilder.properties = @[@"name", @"email"];
queryBuilder.related = @[@"addresses"];
queryBuilder.sortBy = @[@"age"];
[[[Backendless.shared data] of:[Person class]] findFirstWithQueryBuilder:queryBuilder responseHandler:^(Person *person) {
// handle response
} errorHandler:^(Fault *fault) {
// handle error
}];
let queryBuilder = DataQueryBuilder()
queryBuilder.properties = ["name", "email"]
queryBuilder.related = ["addresses"]
queryBuilder.sortBy = ["age"]
Backendless.shared.data.of(Person.self).findFirst(queryBuilder: queryBuilder, responseHandler: { person in
// handle response
}, errorHandler: { fault in
// handle error
})
DataQueryBuilder *queryBuilder = [DataQueryBuilder new];
queryBuilder.properties = @[@"name", @"email"];
queryBuilder.related = @[@"addresses"];
queryBuilder.sortBy = @[@"age"];
[[[Backendless.shared data] ofTable:@"Person"] findFirstWithQueryBuilder:queryBuilder responseHandler:^(NSDictionary *person) {
// handle response
} errorHandler:^(Fault *fault) {
// handle error
}];
Example Find the last object in the "Person" table with the queryBuilder parameter.
DataQueryBuilder *queryBuilder = [DataQueryBuilder new];
queryBuilder.properties = @[@"name", @"email"];
queryBuilder.related = @[@"addresses"];
queryBuilder.sortBy = @[@"age"];
[[[Backendless.shared data] of:[Person class]] findFirstWithQueryBuilder:queryBuilder responseHandler:^(Person *person) {
// handle response
} errorHandler:^(Fault *fault) {
// handle error
}];
let queryBuilder = DataQueryBuilder()
queryBuilder.properties = ["name", "email"]
queryBuilder.related = ["addresses"]
queryBuilder.sortBy = ["age"]
Backendless.shared.data.of(Person.self).findFirst(queryBuilder: queryBuilder, responseHandler: { person in
// handle response
}, errorHandler: { fault in
// handle error
})
DataQueryBuilder *queryBuilder = [DataQueryBuilder new];
queryBuilder.properties = @[@"name", @"email"];
queryBuilder.related = @[@"addresses"];
queryBuilder.sortBy = @[@"age"];
[[[Backendless.shared data] ofTable:@"Person"] findLastWithQueryBuilder:queryBuilder responseHandler:^(NSDictionary *person) {
// handle response
} errorHandler:^(Fault *fault) {
// handle error
}];
Codeless Reference¶
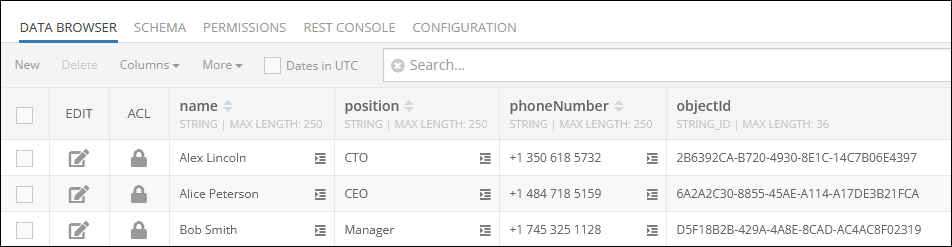
The data table employees presented below is used throughout all Codeless examples as the main reference:
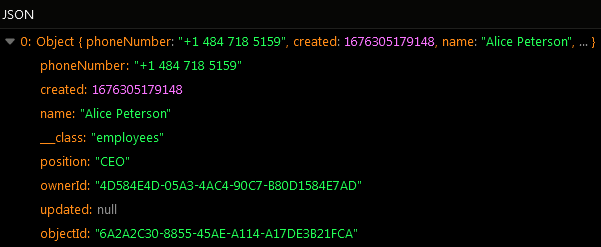
Find First Object¶
The example below retrieves the first object stored in the "employees" data table.
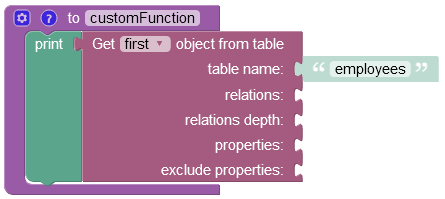
where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
table name |
Name of the data table from where the required object is retrieved. |
relations |
Name of the related property to load. For example, if table employees has a relation column homeAddress pointing to an object in the Address table, the value of the parameter would be homeAddress. The syntax allows to add relations of relations. For example, if the same Address table has a relation country pointing to the Country table, then homeAddress.country would instruct the backend to load the related Country object. |
relations depth |
Depth of the relations to include into the response. |
properties |
Names of the properties/columns for which to load the corresponding values. |
exclude properties |
Names of the properties/columns that should not be included in the response. |
The operation has returned the following result:
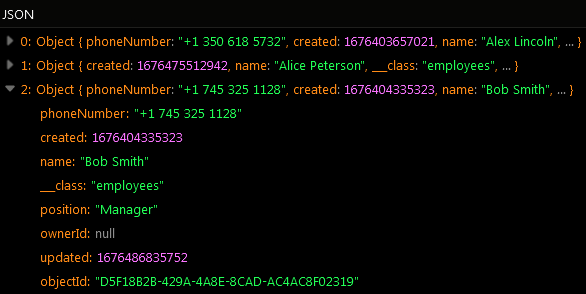
Find Last Object¶
The example below retrieves the last object stored in the "employees" data table.
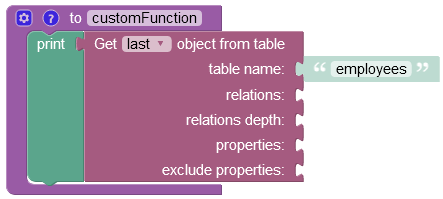
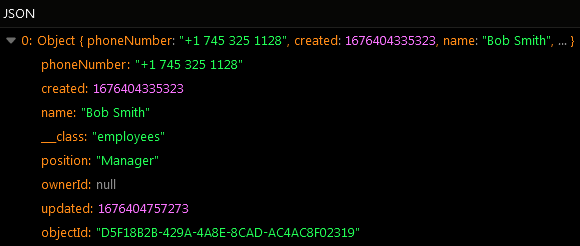
The operation has returned the following result:
Find Object By ID¶
Consider the following scenario where you want to retrieve an object associated with both the object id: "2B6392CA-B720-4930-8E1C-14C7B06E4397" and the name "Alex Lincoln". In the example provided below, the operation searches for an object by its object id and returns it as part of the response:
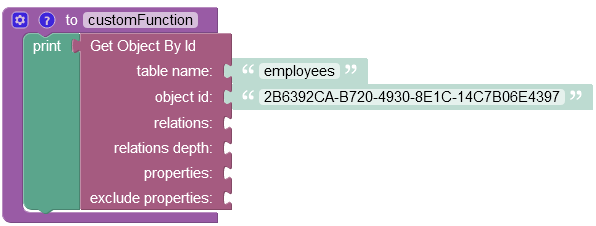
where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
table name |
Name of the data table from where the required object is retrieved. |
object id |
Unique identifier of the object to retrieve. |
relations |
Name of the related property to load. For example, if table employees has a relation column homeAddress pointing to an object in the Address table, the value of the parameter would be homeAddress. The syntax allows to add relations of relations. For example, if the same Address table has a relation country pointing to the Country table, then homeAddress.country would instruct the backend to load the related Country object. |
relations depth |
Depth of the relations to include into the response. |
properties |
Names of the properties/columns for which to load the corresponding values. |
exclude properties |
Names of the properties/columns that should not be included in the response. |
The result of this operation will look as shown below after the Codeless logic runs.
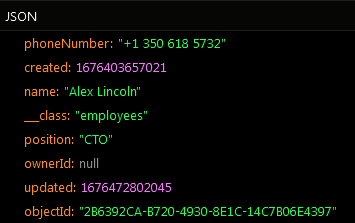
Load All Objects From Data Table¶
The example below loads all objects from the employees data table.
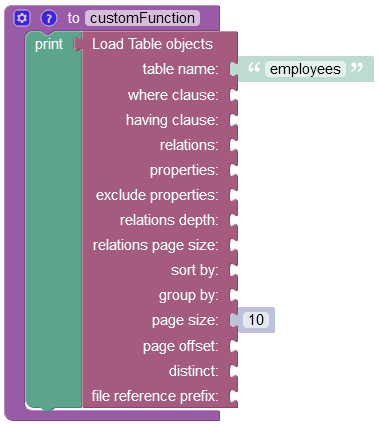
where:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
table name |
Name of the data table from where the objects are retrieved. |
where clause |
A search query used by the server it to determine objects matching the condition. Refer to the Search With The Where Clause topic for more information. |
having clause |
Sets a condition on a aggregate function to filter groups. |
relations |
Name of the related property to load. For example, if table employees has a relation column homeAddress pointing to an object in the Address table, the value of the parameter would be homeAddress. The syntax allows to add relations of relations. For example, if the same Address table has a relation country pointing to the Country table, then homeAddress.country would instruct the backend to load the related Country object. |
properties |
Names of the properties/columns for which to load the corresponding values. |
exclude properties |
Names of the properties/columns that should not be included in the response. |
relations depth |
Depth of the relations to include into the response. |
relations page size |
Sets the number of related objects returned in the response. |
sort by |
Lists properties by which the returned collection should be sorted by. |
group by |
Sets the name of the columns to group the results by. |
page size |
Sets the page size which is the number of objects to be returned in the response. |
page offset |
Zero-based index of the object in the persistent store from which to run the search. This parameter should be used when implementing paged access to data. Suppose the first request returned 20 objects (if pageSize is set to 20) and there are 100 objects total. The subsequent request can set offset to 20, so the next batch of objects is loaded sequentially. |
distinct |
Used to return only unique values from a column. |
file reference prefix |
This property allows replacing the default URL file prefix. For instance, when the operation returns a path to a file stored on the server ("https://yourdomain.backendless.app/my-file.jpg"), then you can reconstruct it by passing the new file name that must start with a slash - "/wonderful_forest.jpg". It is useful when you want the client application to open a specific file locally. |
The result of this operation will look as shown below after the Codeless logic runs.